下拉有很多__【询价/阅新品 + 右侧联系】
工厂效果图制作案件:
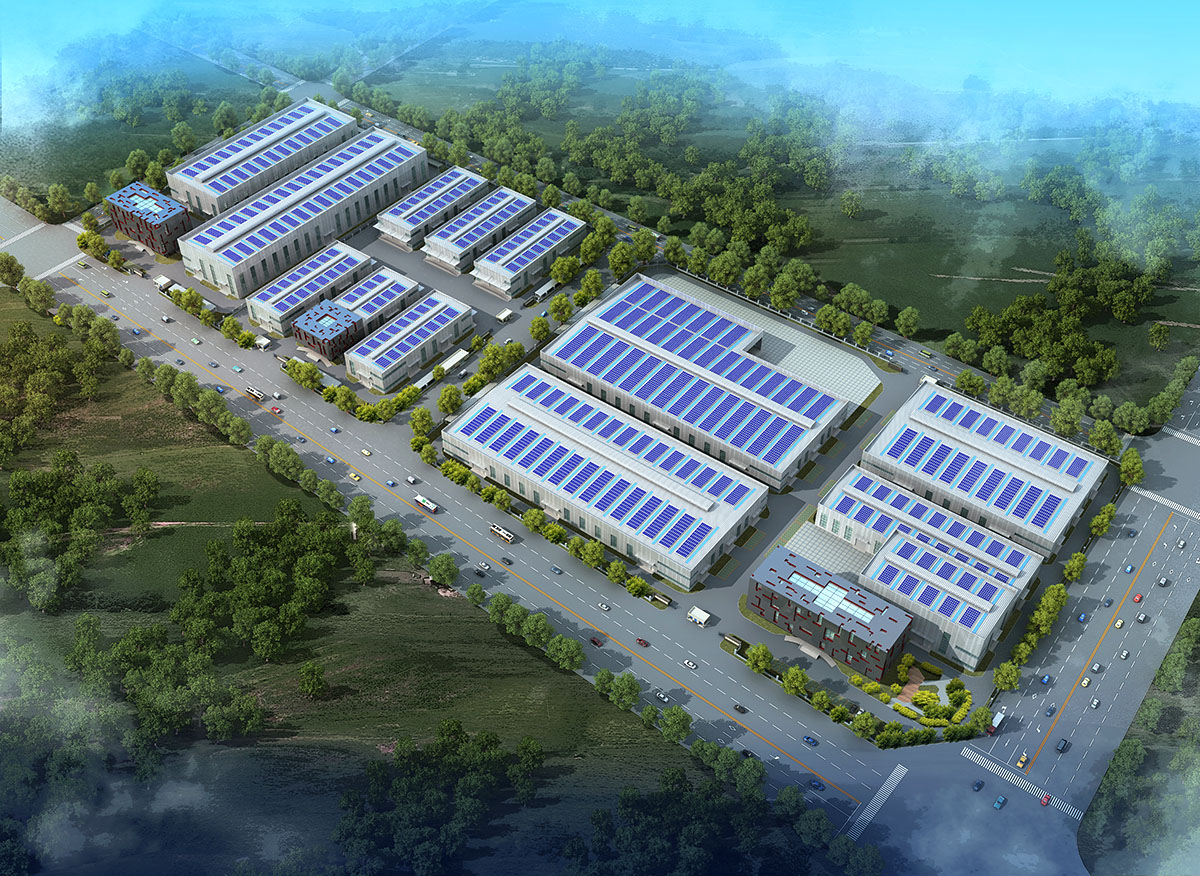
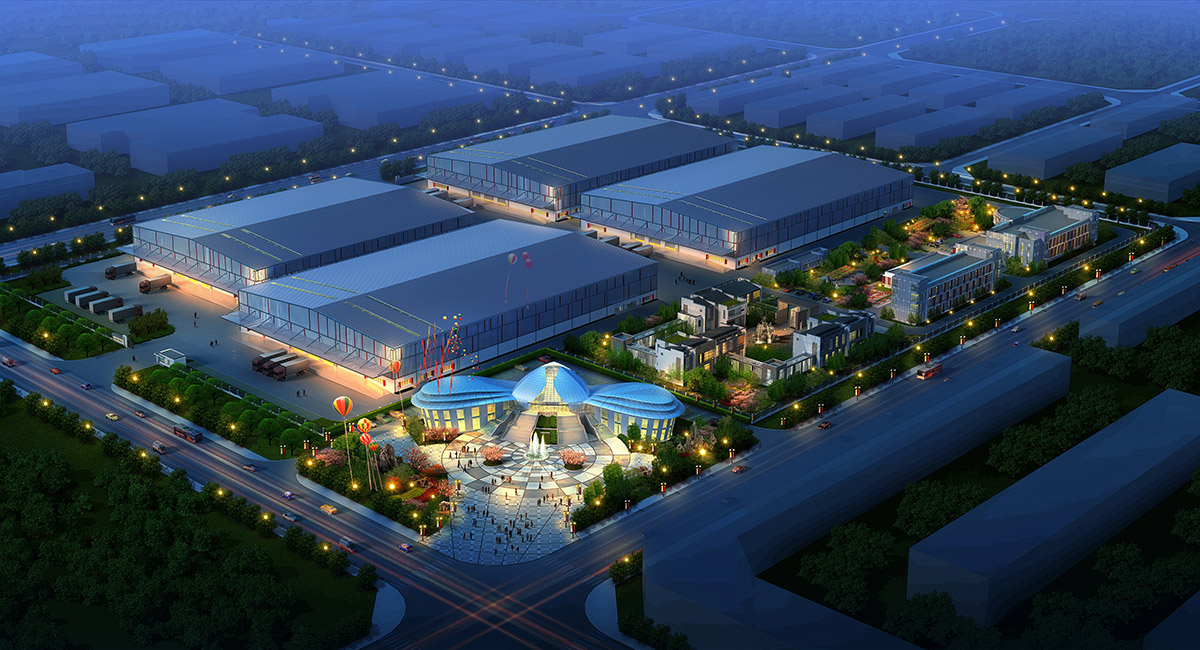
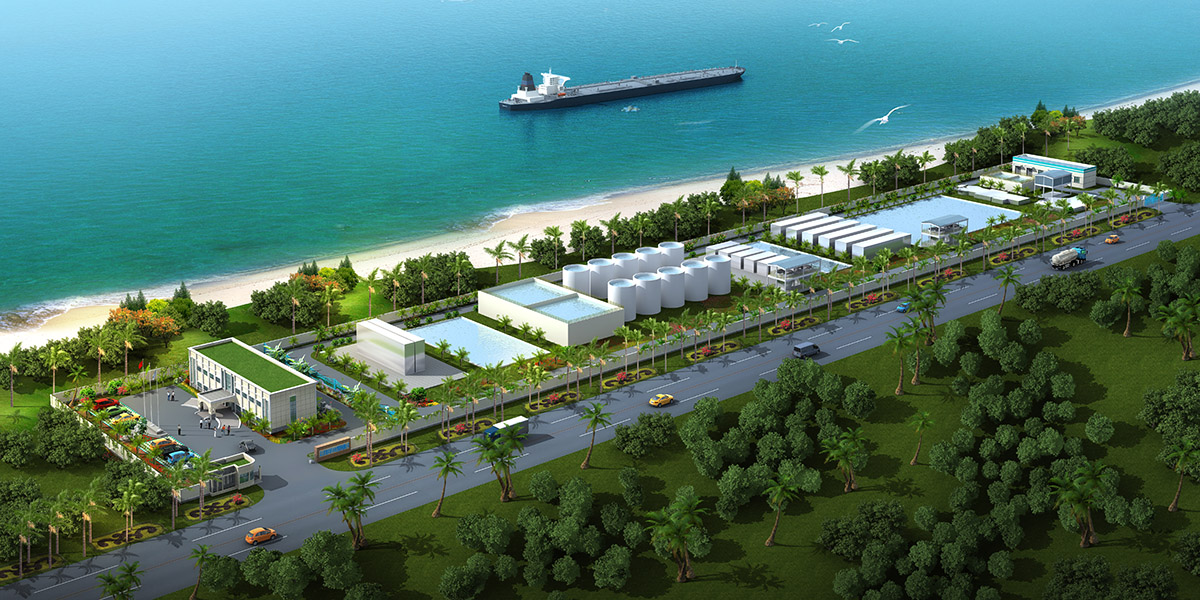
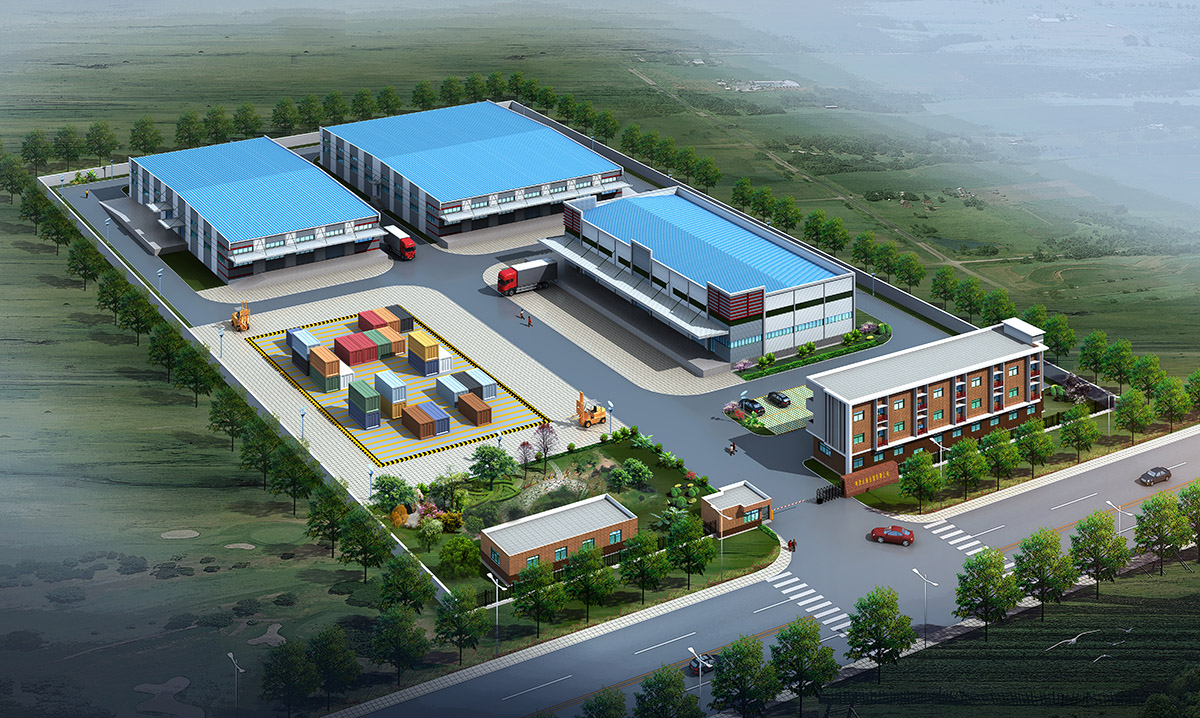
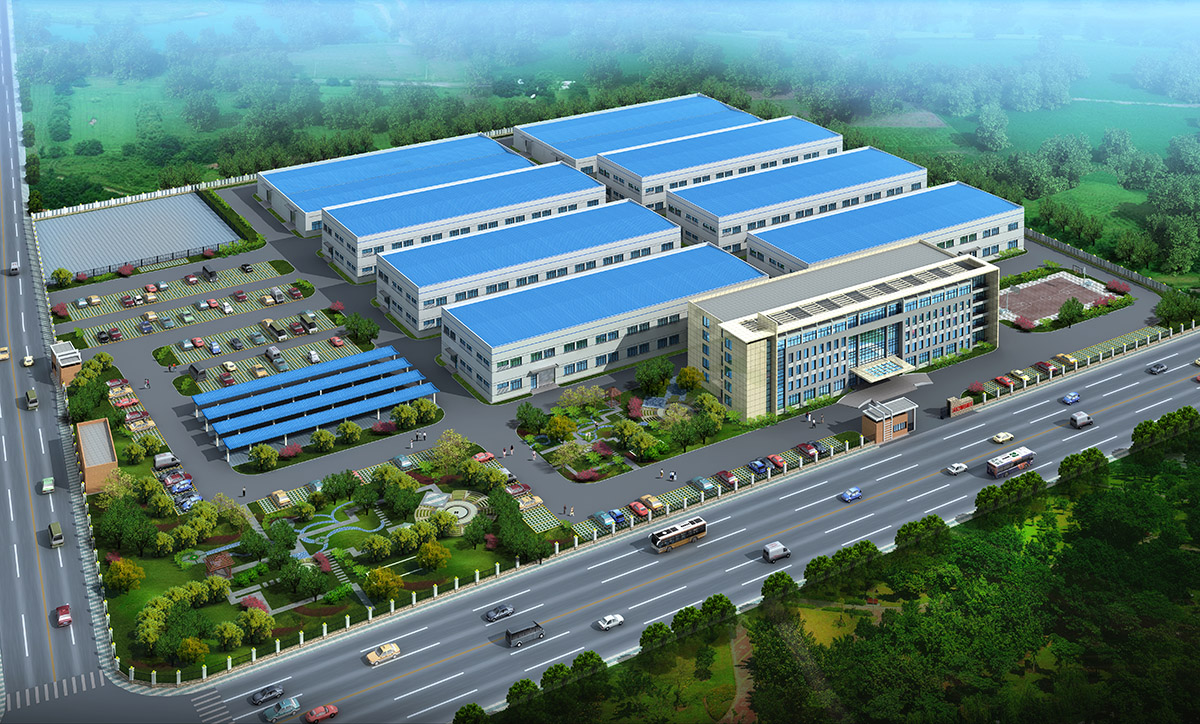
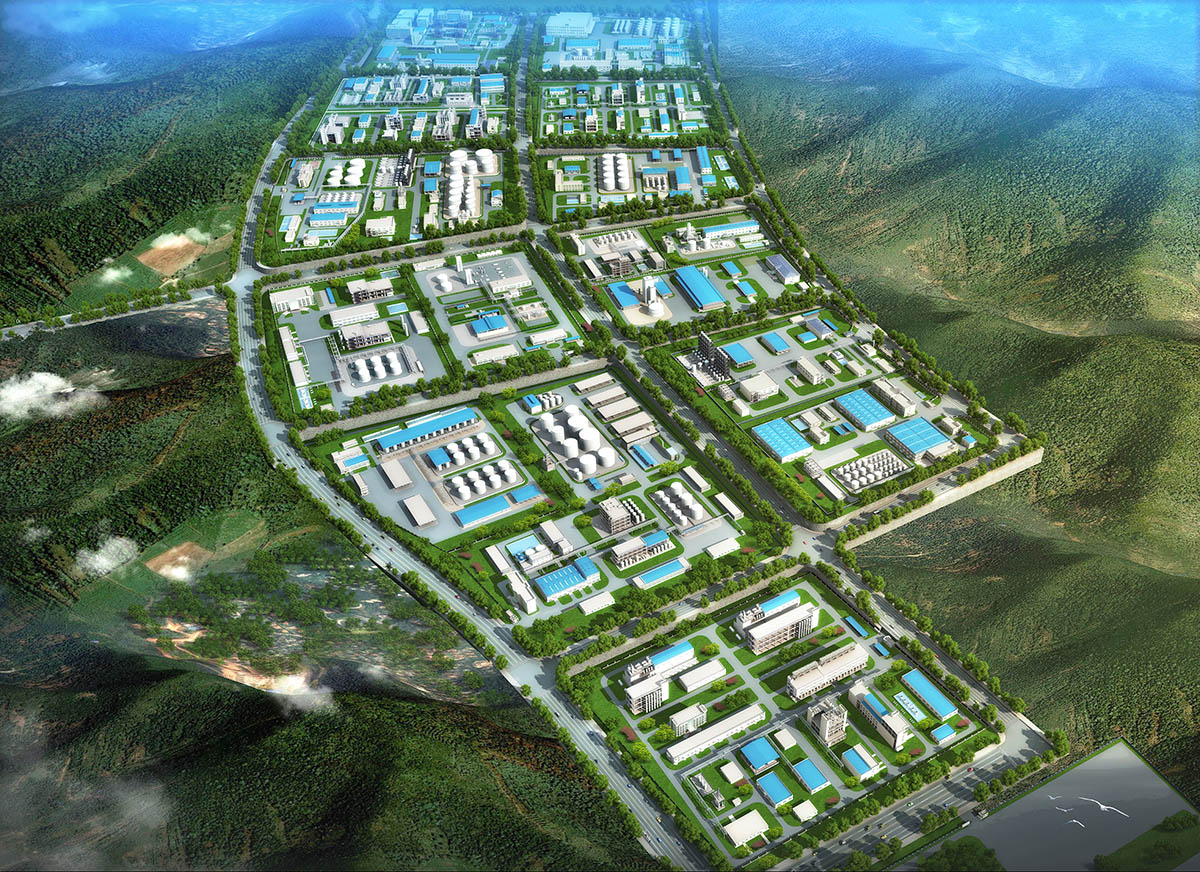
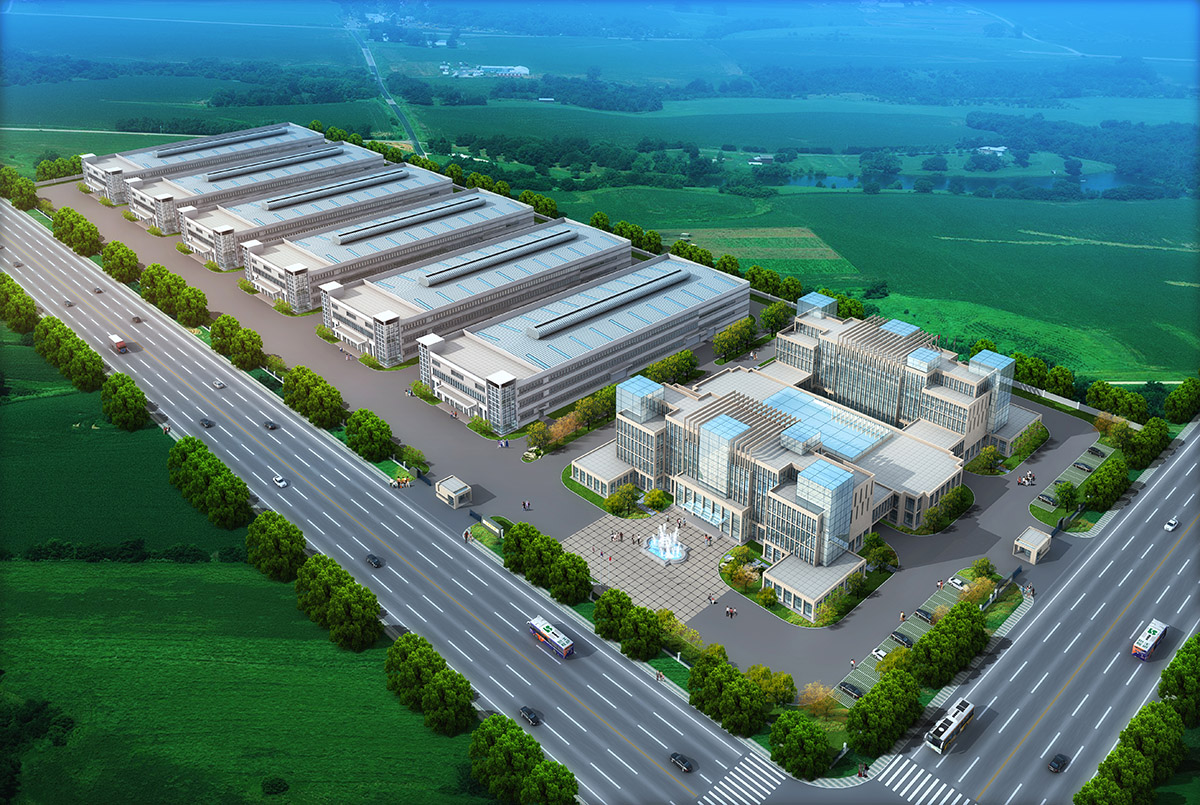
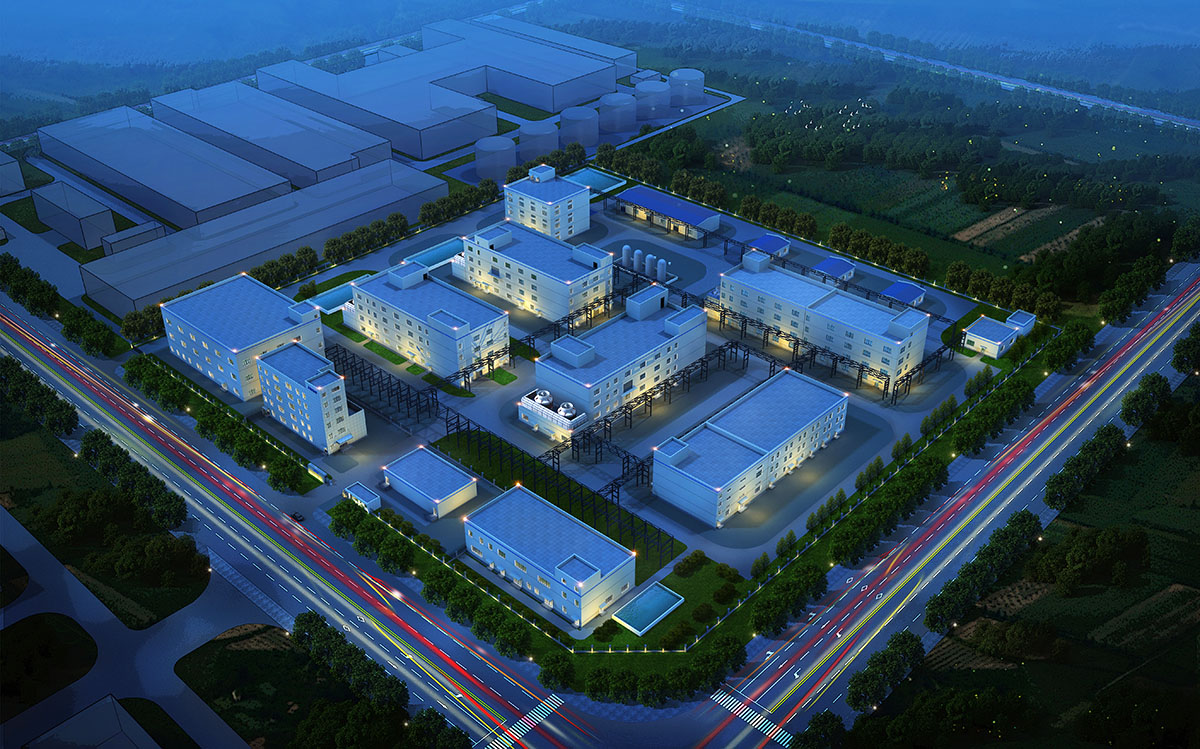
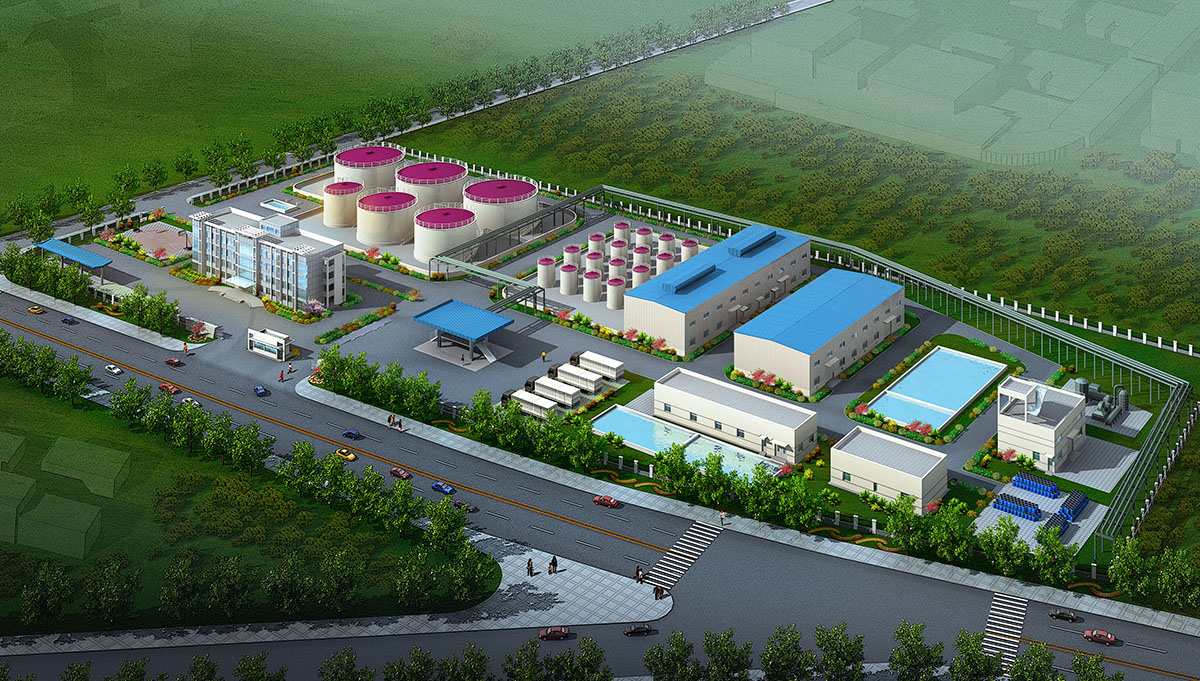
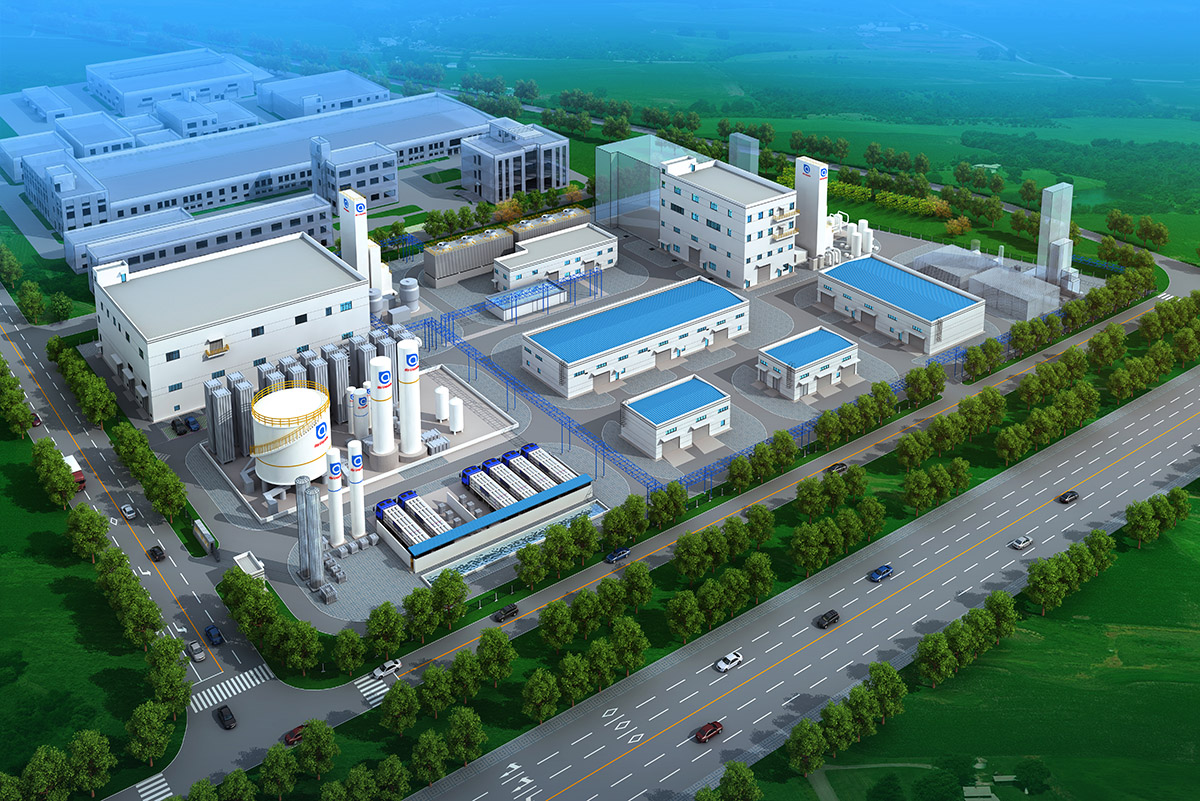
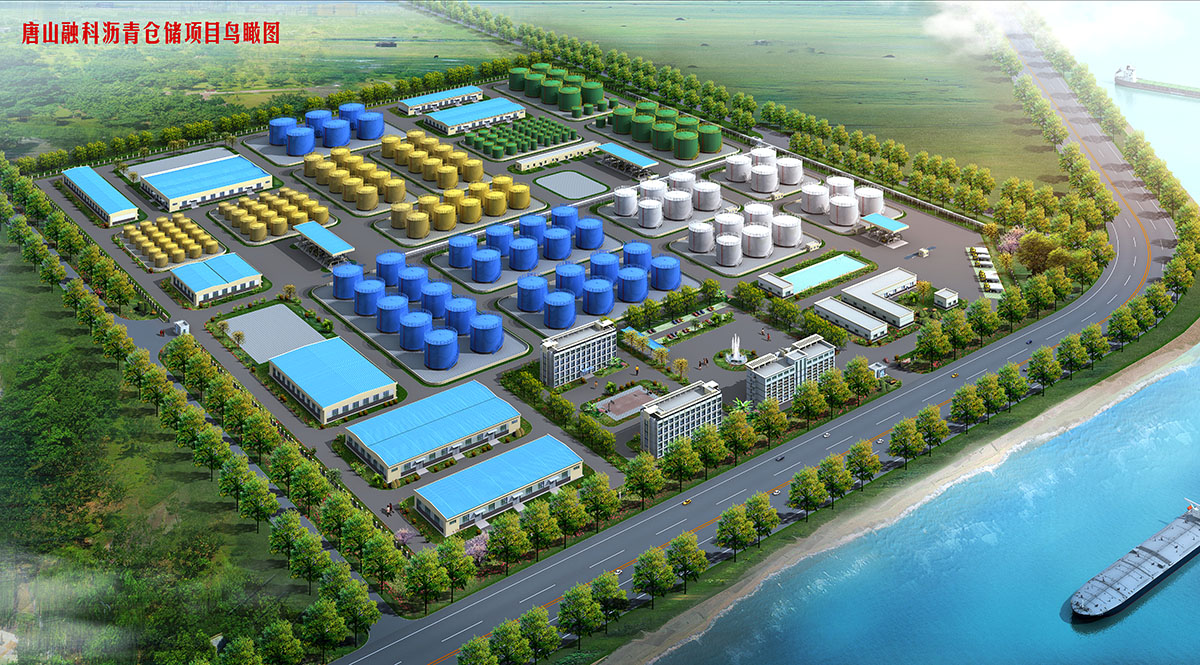
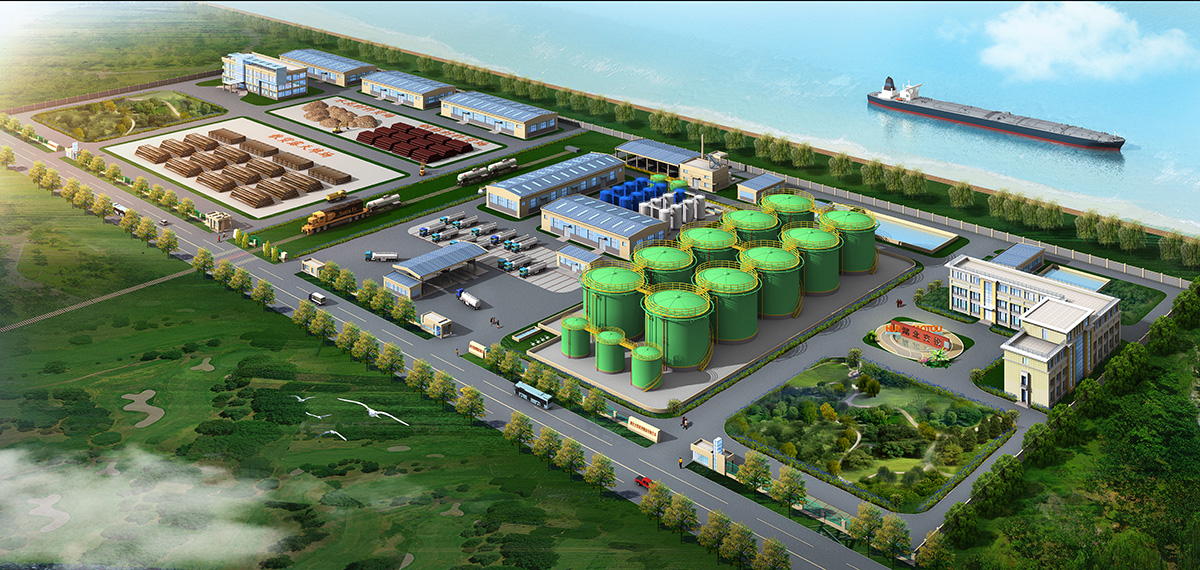
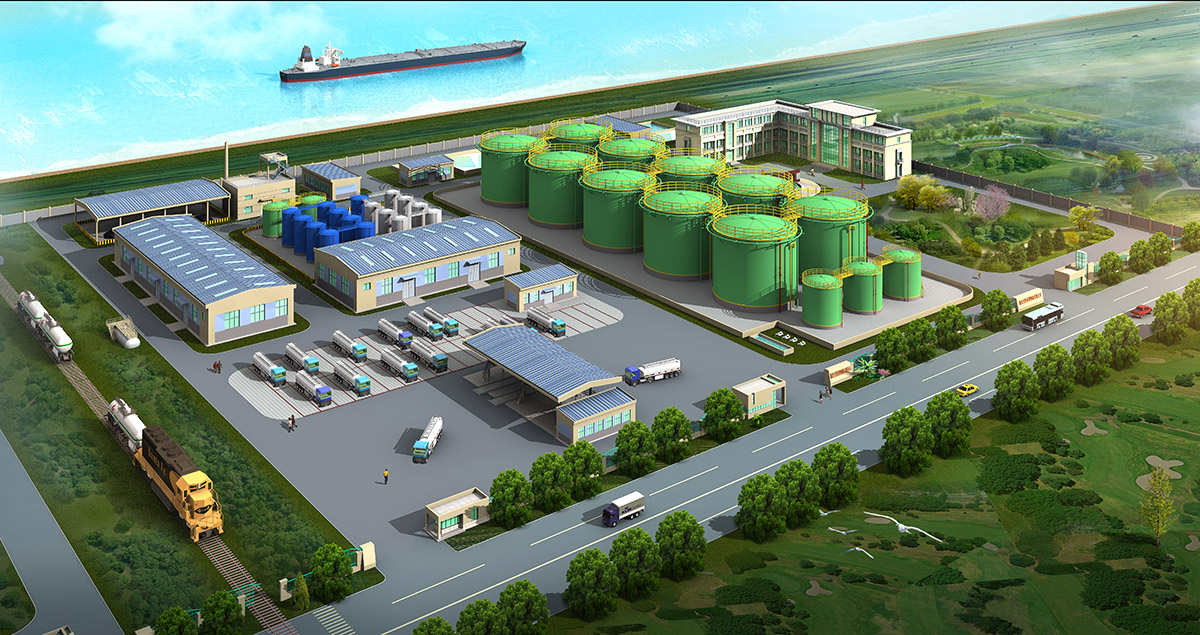
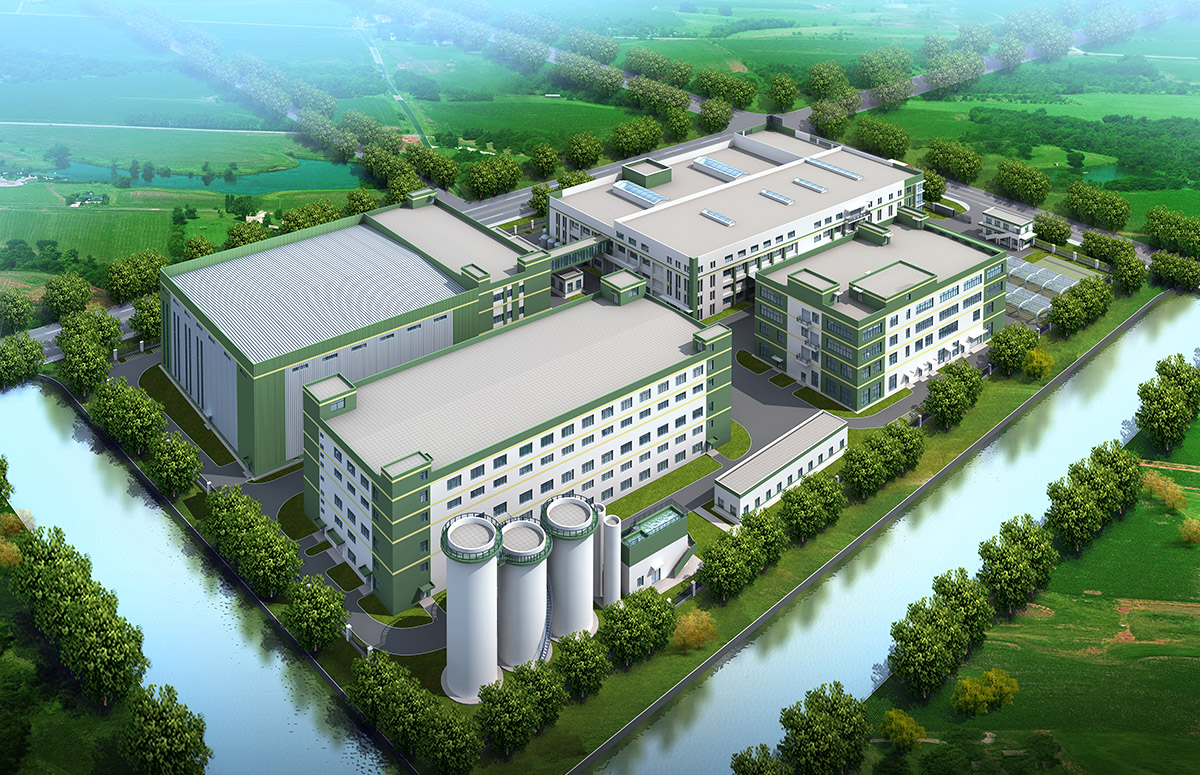
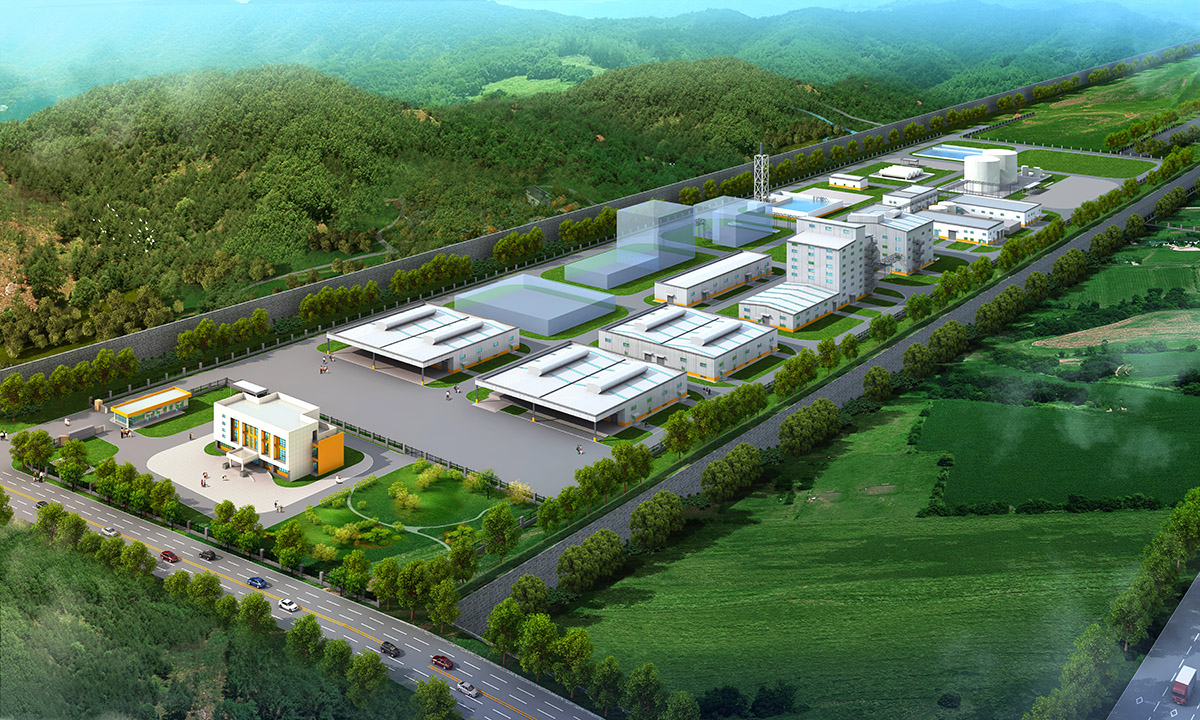
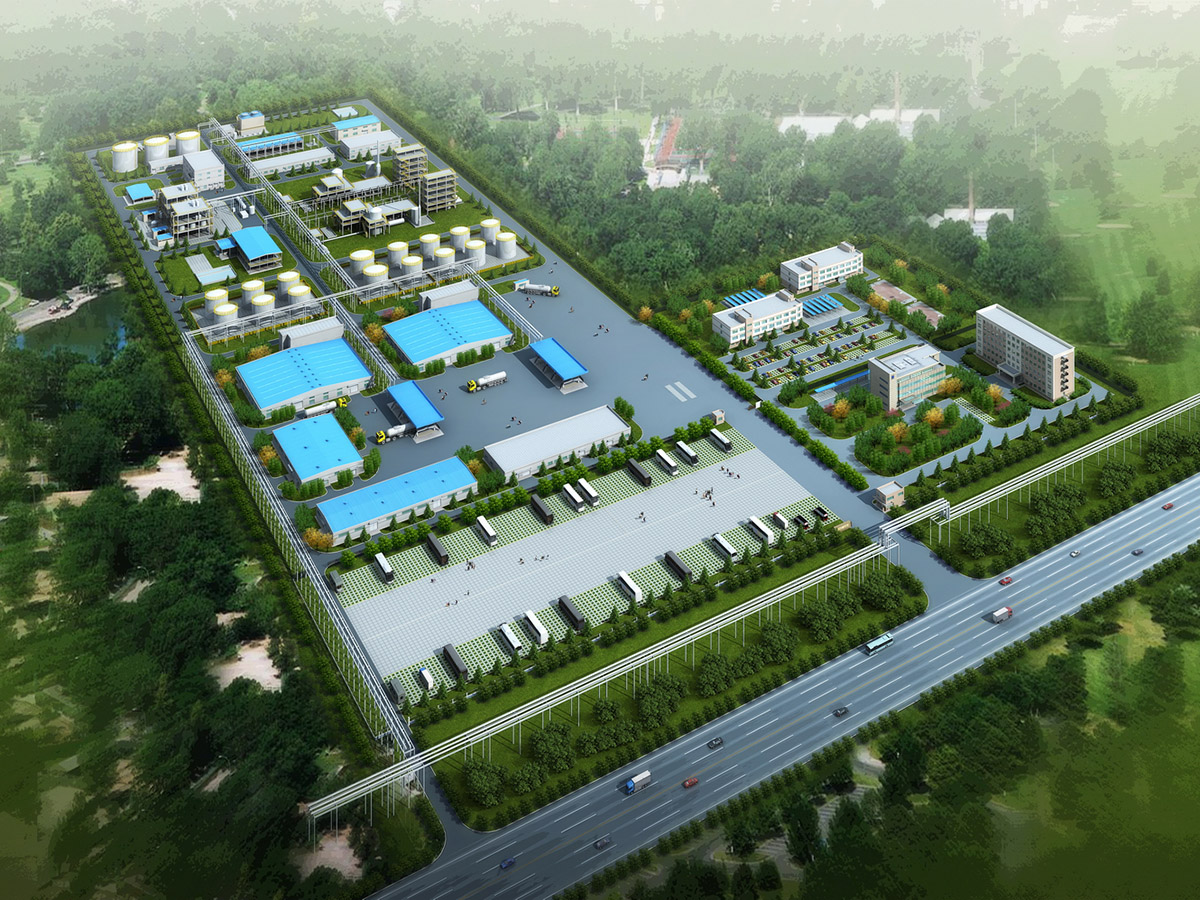



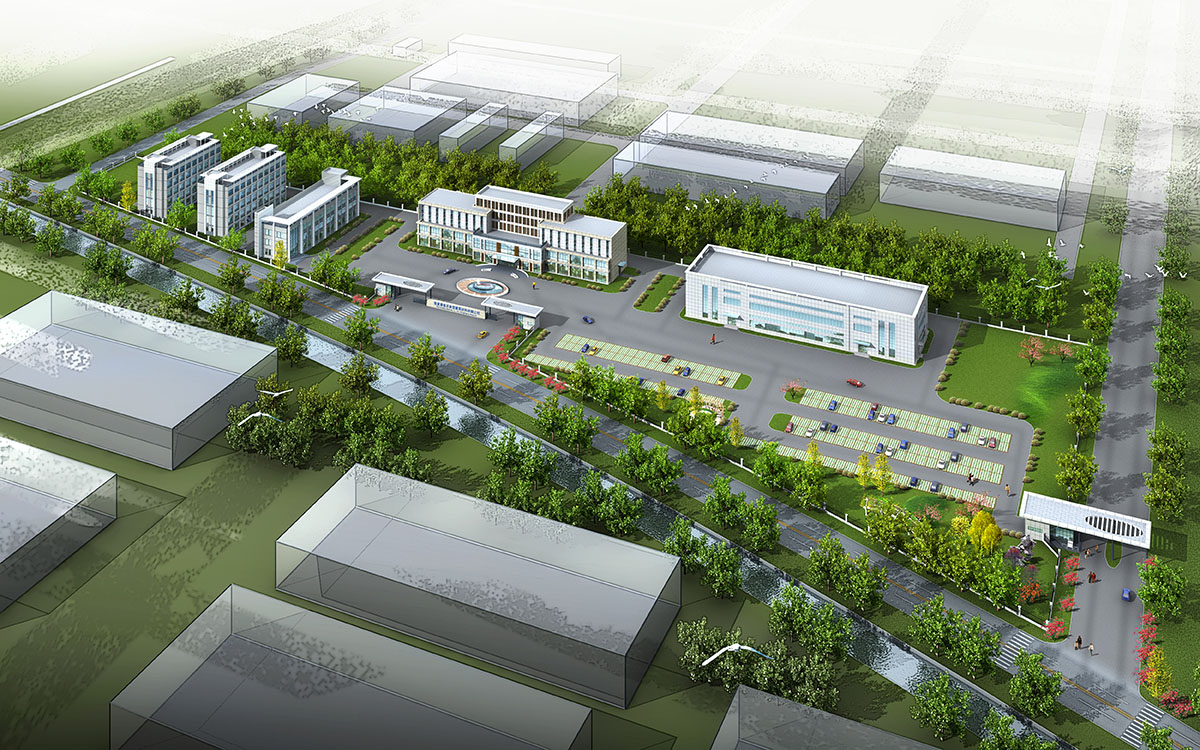




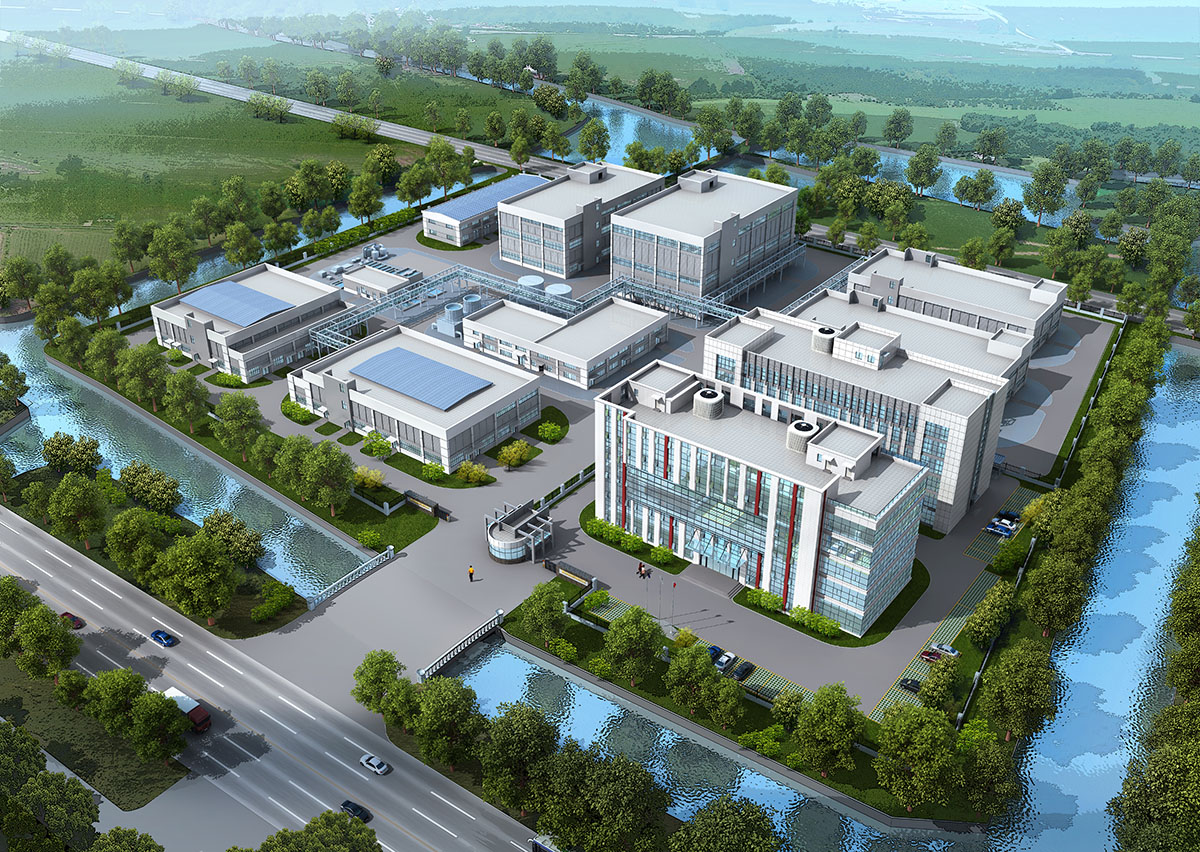



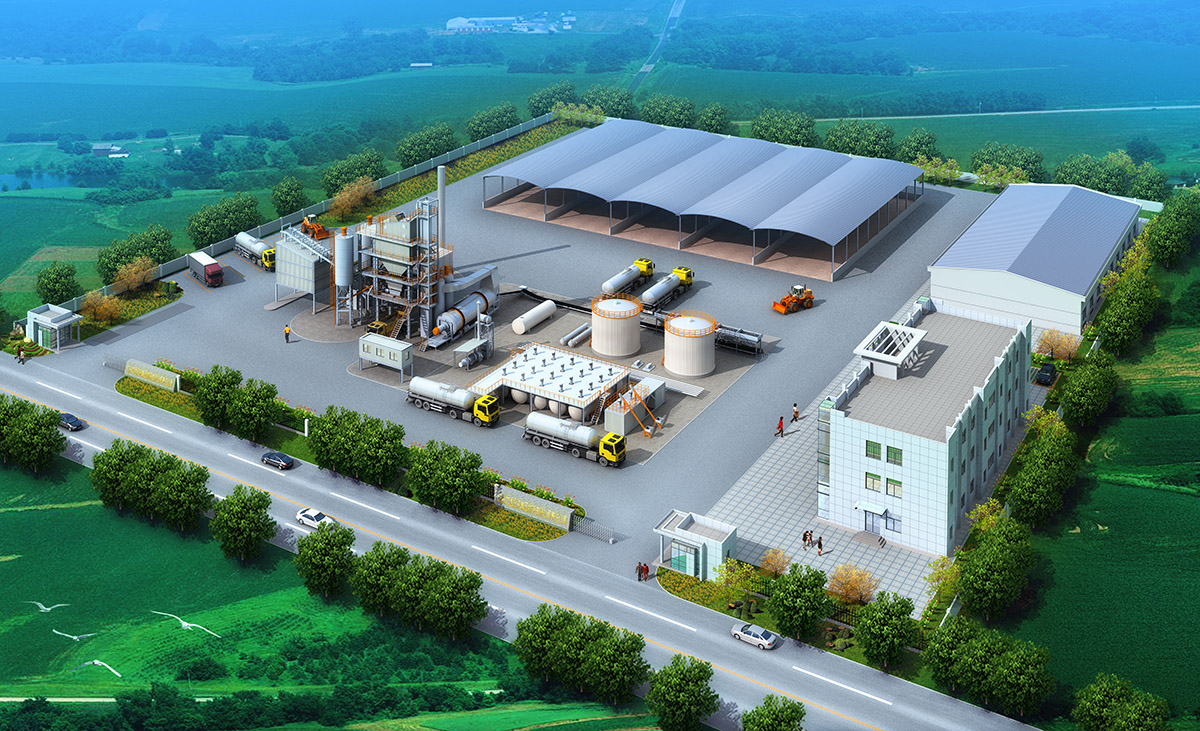






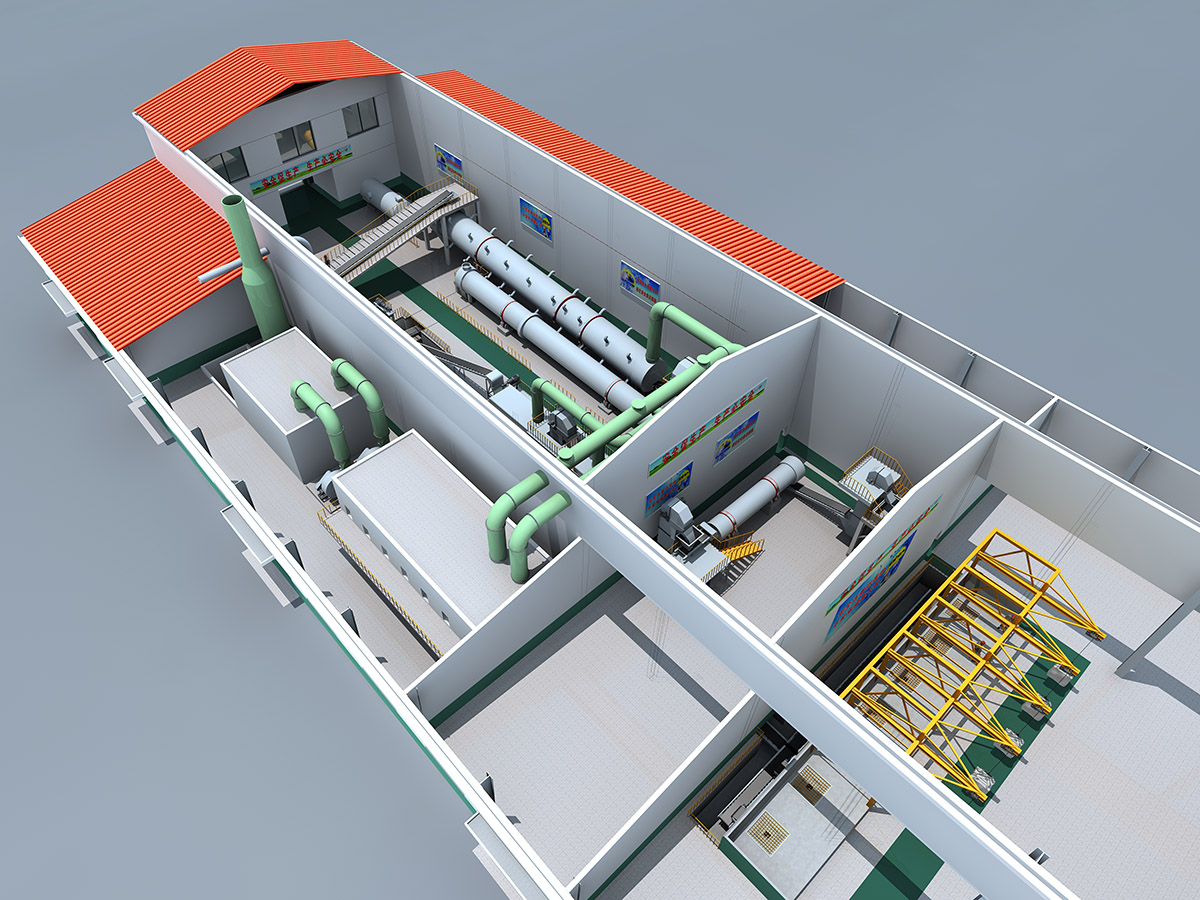
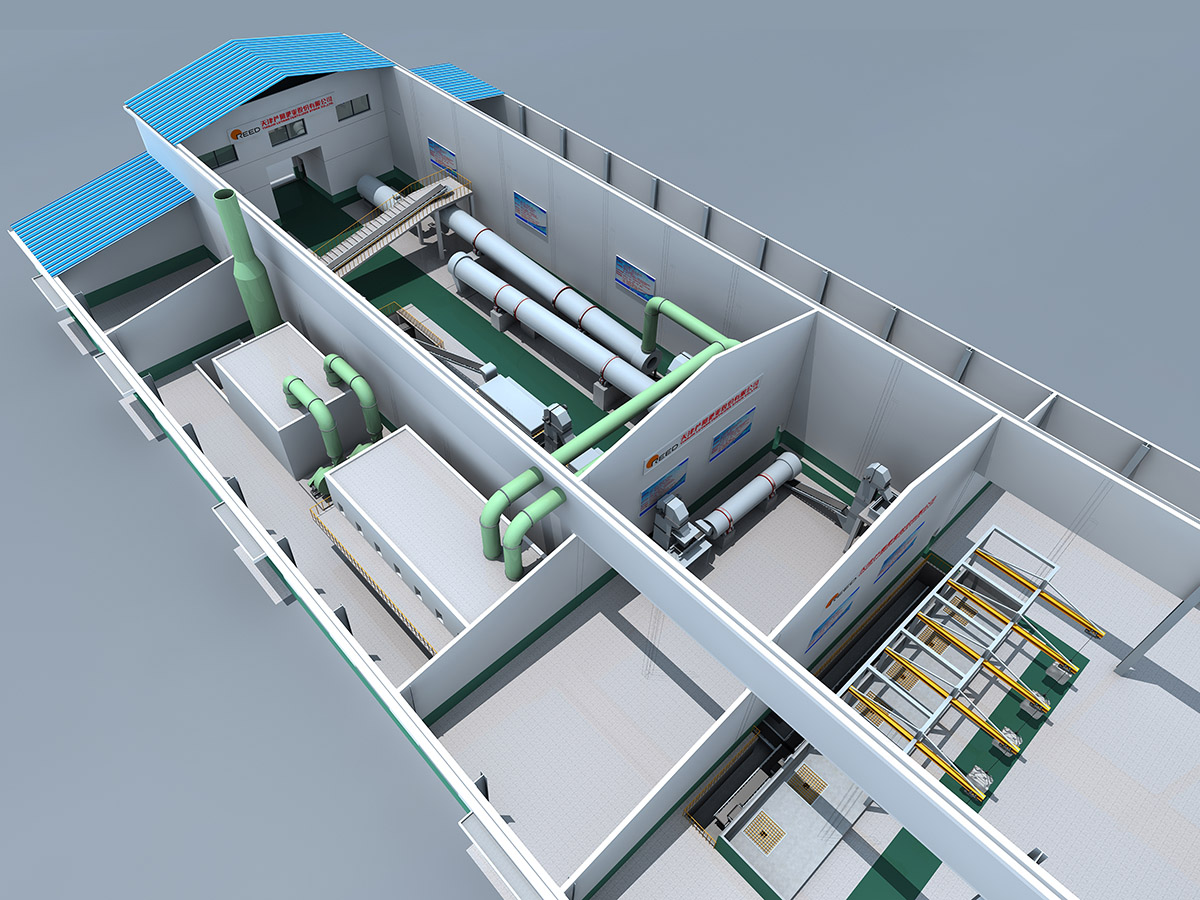
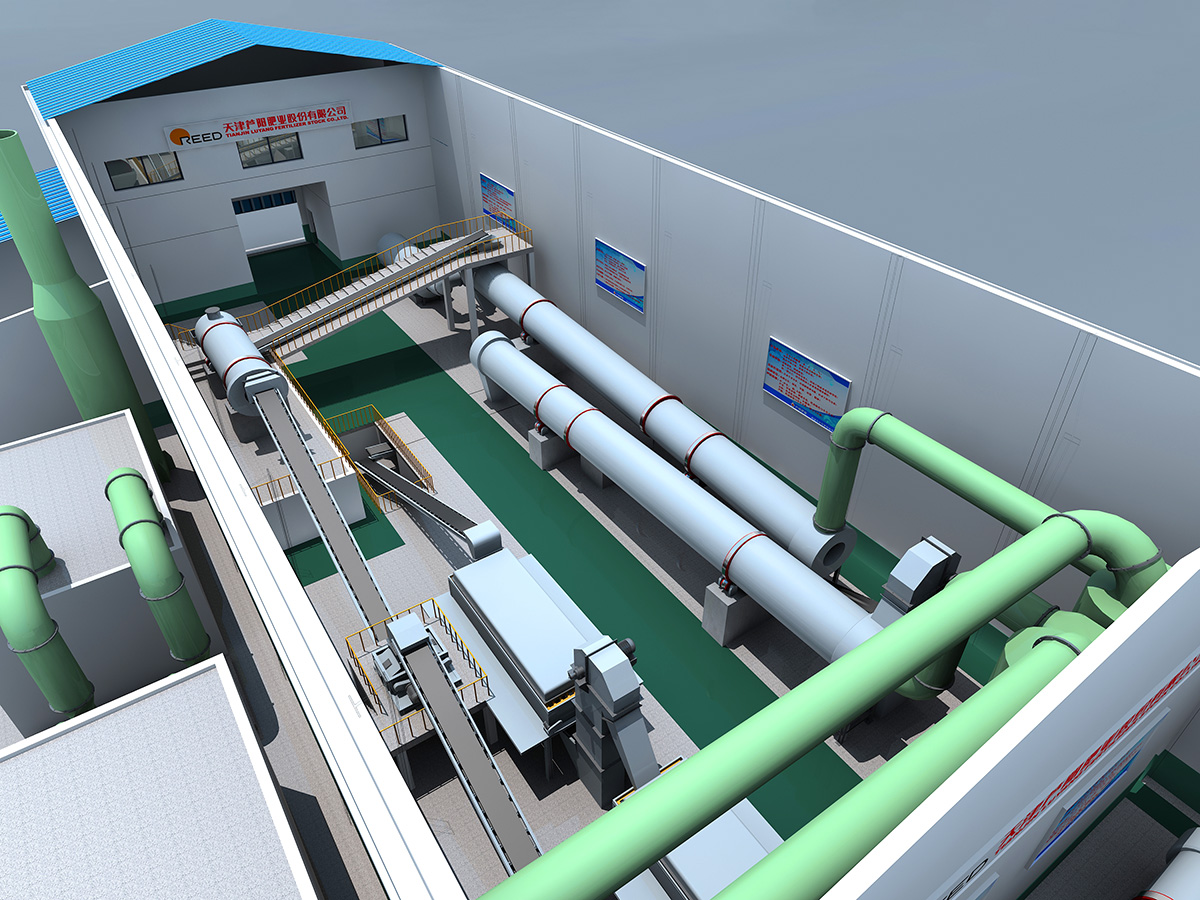
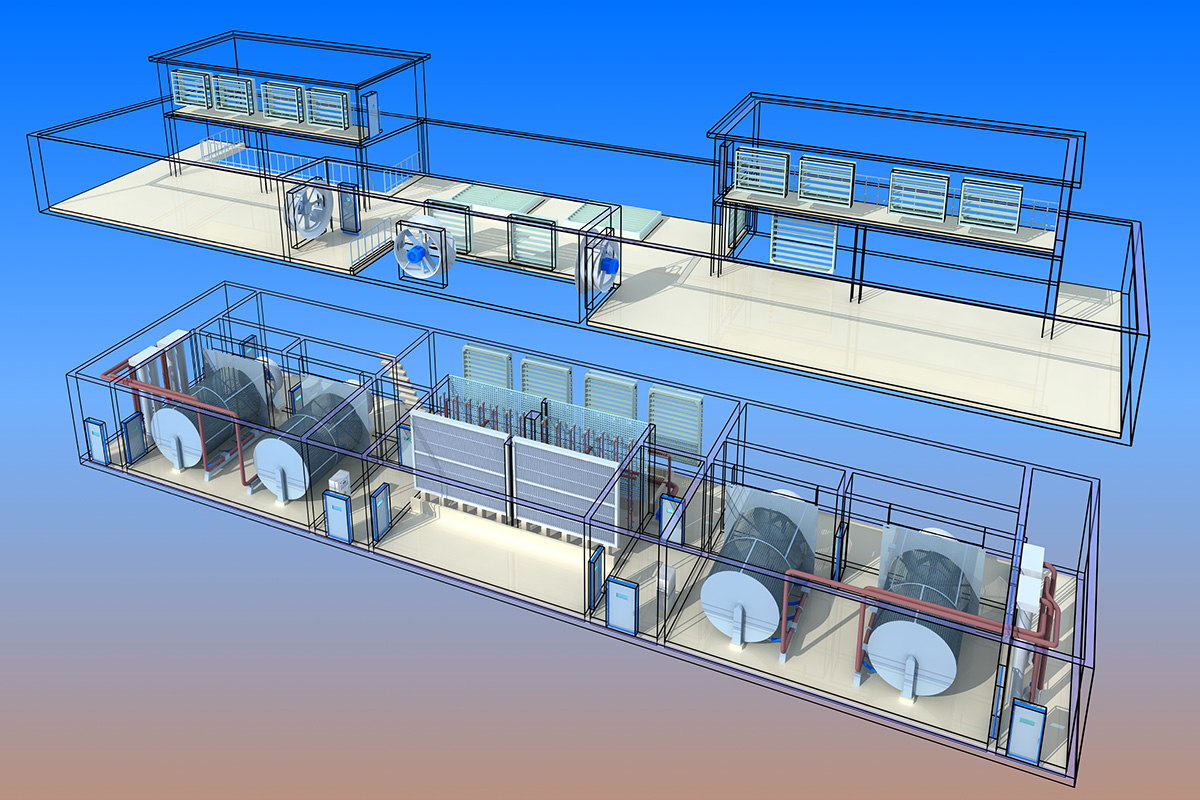
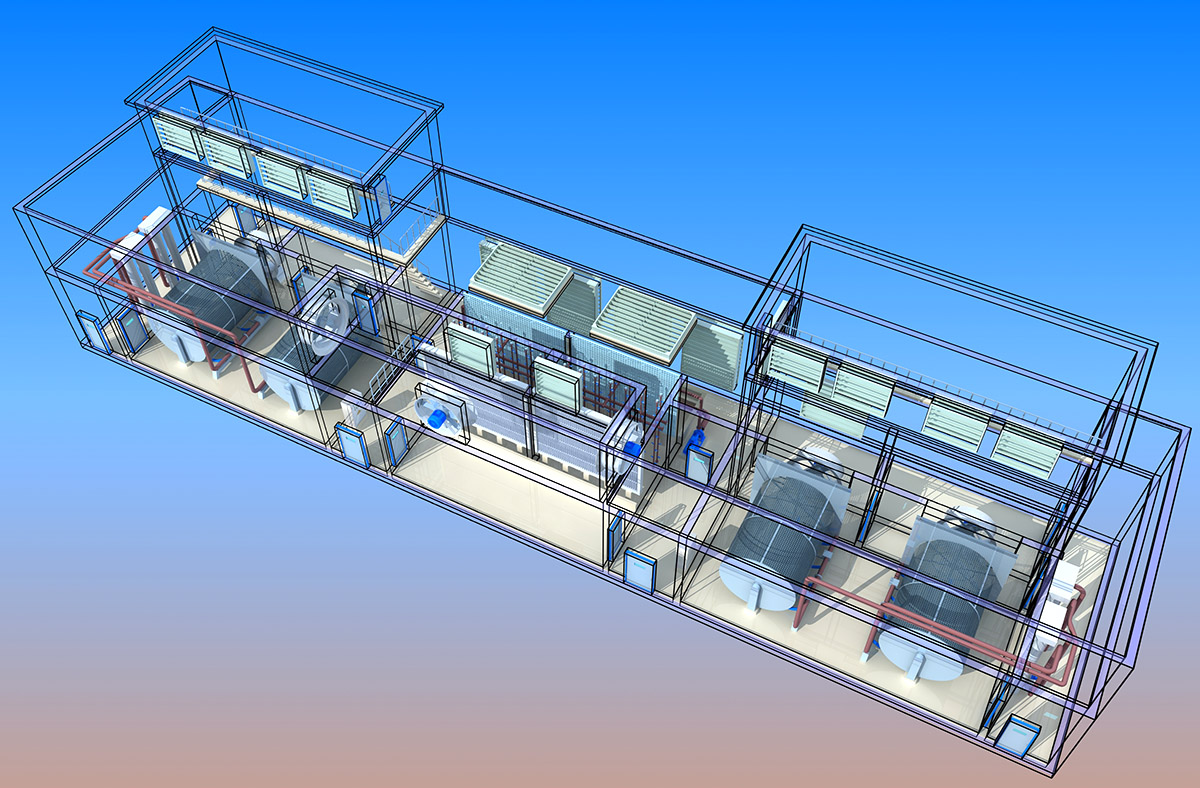
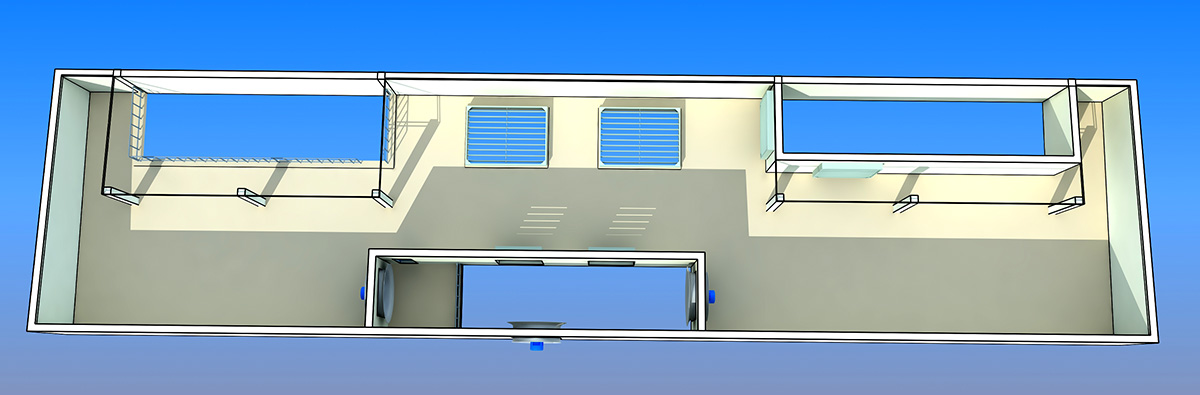
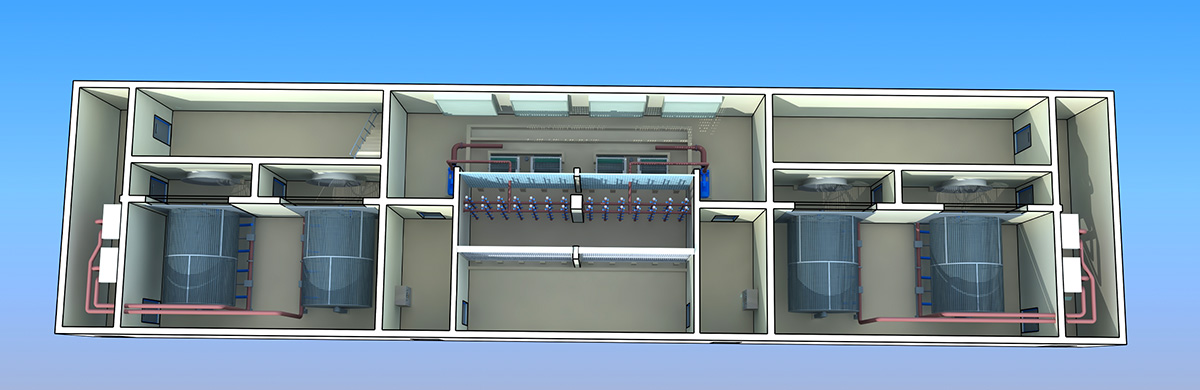
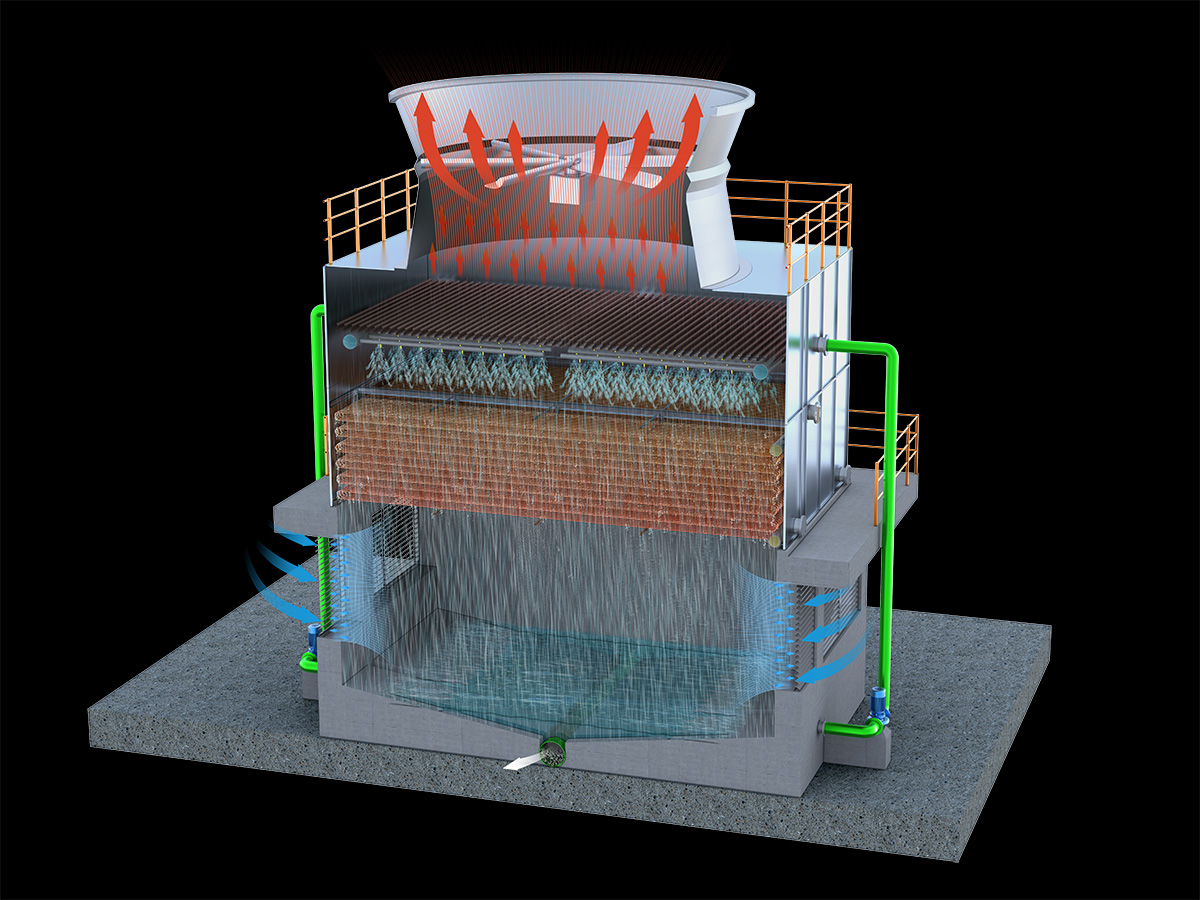
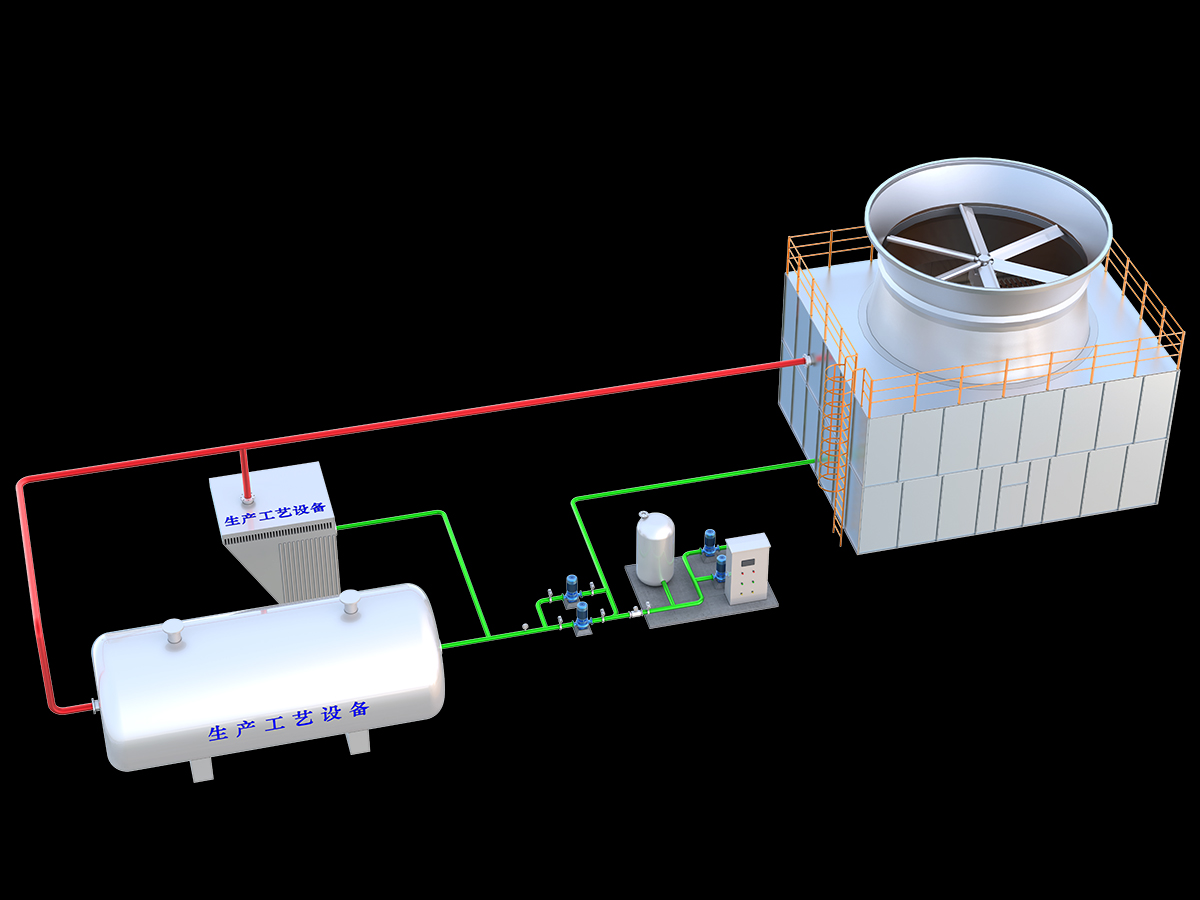





厂房效果图制作根据应用场景、展示重点及用户需求的不同,可划分为以下分类,每个分类都具备独特的应用价值:
一、按应用场景分类
项目规划阶段效果图
核心用途:在厂房建设初期,用于展示整体规划布局、建筑风格及周边环境关系。
特点:侧重宏观视角,突出厂房与周边地形、交通的协调性,为决策者提供直观参考。
案例:开发区厂房群规划效果图,需清晰呈现各厂房功能分区及物流动线。
招商引资效果图
核心用途:吸引投资者关注,展示厂房生产环境、配套设施及区位优势。
特点:强调厂房现代化程度、空间利用率及周边产业集群效应,需突出投资回报潜力。
案例:工业园区厂房效果图,需标注交通便利性、政策扶持等关键信息。
施工指导效果图
核心用途:为施工团队提供精确的建筑结构、设备安装及管线布局指导。
特点:注重细节标注,如承重结构、设备基础尺寸及管线走向,需与施工图纸严格对应。
案例:重工业厂房效果图,需明确标注大型设备安装位置及吊装路径。
企业宣传效果图
核心用途:提升企业形象,展示厂房生产能力、技术创新及环保理念。
特点:突出厂房外观的科技感、内部生产线的自动化程度及环保设施,需体现企业核心竞争力。
案例:智能制造企业厂房效果图,需展示智能仓储、机器人生产线等场景。
二、按展示重点分类
建筑外观效果图
核心用途:展示厂房建筑风格、材质及色彩搭配。
特点:强调建筑立面设计、屋顶造型及周边景观融合,需体现建筑美学。
案例:现代风格厂房效果图,需突出玻璃幕墙、金属线条等设计元素。
内部布局效果图
核心用途:展示厂房内部空间规划、设备布局及物流动线。
特点:注重功能分区合理性、设备摆放效率及人员操作便利性,需体现生产流程优化。
案例:食品加工厂房效果图,需明确生产区、仓储区、检验区等功能分区。
设备安装效果图
核心用途:指导大型设备安装位置、基础尺寸及管线连接。
特点:需精确标注设备尺寸、安装高度及管线走向,确保施工精度。
案例:化工设备厂房效果图,需明确反应釜、管道等设备的安装位置及连接方式。
三、按用户需求分类
政府审批需求效果图
核心用途:满足政府规划部门对厂房建设的审批要求。
特点:需符合相关规范标准,如建筑高度、容积率、绿化率等,需提供详细的技术参数。
案例:提交给住建局的厂房规划效果图,需标注建筑红线、退让距离等关键信息。
客户定制需求效果图
核心用途:根据客户个性化需求定制厂房设计方案。
特点:需充分沟通客户生产流程、设备类型及特殊需求,提供定制化解决方案。
案例:为某新能源企业定制的厂房效果图,需满足电池生产线的特殊环境要求。
投资分析需求效果图
核心用途:为投资者提供厂房建设的经济效益分析依据。
特点:需展示厂房建设成本、运营成本及预期收益,需进行财务模型测算。
案例:为投资机构提供的厂房效果图,需包含投资回报率、回收期等关键指标。
工厂效果图作为展示工厂设计方案、规划布局和未来外观的重要工具,具有以下显著优点:
一、直观展示设计成果
三维立体呈现:工厂效果图通过三维建模技术,将工厂的外观、内部结构、设备布局等以立体形式展现出来,使决策者、投资者和设计团队能够直观地看到设计成果,无需通过复杂的文字描述或二维图纸来想象。
细节清晰可见:效果图能够精细地呈现工厂的各个细节,如建筑外观的材质、颜色,内部设备的型号、位置,以及生产线的布局等,为决策者提供全面的信息支持。
二、便于沟通与决策
促进多方沟通:工厂效果图为设计师、工程师、投资者和管理层提供了一个共同的沟通平台,有助于各方就设计方案进行深入讨论,及时发现问题并调整优化。
辅助决策制定:通过效果图,决策者可以更直观地评估设计方案的可行性和经济性,从而做出更加明智的决策。
三、优化设计方案
提前发现潜在问题:在效果图制作过程中,设计师可以模拟工厂的实际运行情况,提前发现设计中可能存在的问题,如空间布局不合理、设备冲突等,并及时进行调整。
优化资源配置:通过效果图,可以更清晰地规划工厂的资源分配,如人员流动路线、物料运输路径等,提高生产效率,降低运营成本。
四、提升项目吸引力
增强项目可信度:专业的工厂效果图能够展示项目的专业性和可行性,提升投资者和合作伙伴对项目的信心。
吸引潜在客户:对于需要展示工厂实力的企业来说,效果图是一种有效的宣传手段,可以吸引潜在客户的关注,促进业务合作。
五、支持施工规划与指导
明确施工要求:效果图为施工团队提供了明确的施工指导,包括建筑结构、设备安装位置、管线布局等,有助于施工团队更准确地理解设计意图,减少施工过程中的误解和错误。
优化施工流程:通过效果图,施工团队可以提前规划施工流程,合理安排施工顺序,提高施工效率,缩短工期。
厂房效果图制作是一项综合性的技术工作,涉及多个领域的技能和知识。以下是制作厂房效果图所需的主要技能:
一、基础技能
三维建模能力
核心要求:熟练掌握3D建模软件(如3ds Max、Maya、SketchUp等),能够根据设计图纸或草图创建厂房的三维模型。
技能要点:
熟悉多边形建模、曲面建模等技术。
能够准确还原厂房的建筑结构、设备布局及细节特征。
掌握模型优化技巧,确保渲染效率。
材质与纹理应用
核心要求:理解不同材质的物理特性(如金属、混凝土、玻璃等),能够通过材质编辑器模拟真实效果。
技能要点:
掌握UV展开技术,确保纹理贴图准确映射。
熟悉PBR(基于物理的渲染)材质流程,提升材质真实感。
灯光与渲染技术
核心要求:掌握灯光布置原则,能够模拟自然光、人工光及环境光效果。
技能要点:
熟悉全局光照、HDRI环境贴图等技术。
掌握渲染器(如V-Ray、Corona、Arnold等)的使用,优化渲染参数。
能够平衡渲染质量与效率,满足项目需求。
二、设计技能
空间规划与布局能力
核心要求:理解厂房功能分区(如生产区、仓储区、办公区等),能够合理规划空间动线。
技能要点:
掌握人体工程学原理,优化人员操作与设备布局。
熟悉物流动线设计,提升生产效率。
色彩与美学设计
核心要求:具备色彩搭配能力,能够通过色彩提升厂房视觉效果。
技能要点:
理解色彩心理学,选择符合厂房功能的配色方案。
掌握光影对比与视觉焦点设计,增强画面层次感。
风格化设计能力
核心要求:根据厂房类型(如工业风、现代风、科技风等)调整设计风格。
技能要点:
熟悉不同风格的建筑特征与材质表现。
能够通过后期处理强化风格化效果(如色调调整、光影强化等)。
三、软件技能
三维建模软件
主流工具:3ds Max、Maya、SketchUp、Rhino等。
技能要求:
熟练掌握建模、材质、灯光等基础功能。
能够通过插件(如Forest Pack、RailClone等)提升效率。
渲染软件
主流工具:V-Ray、Corona、Arnold、Lumion等。
技能要求:
掌握渲染参数优化技巧,平衡质量与速度。
熟悉后期处理流程(如Photoshop调色、合成等)。
辅助工具
CAD软件:AutoCAD用于读取设计图纸,确保建模精度。
图像处理软件:Photoshop用于后期调色、合成与细节优化。
动画软件:如需制作动态效果图,需掌握After Effects、Premiere等工具。
四、行业知识
厂房设计规范
核心要求:了解厂房建设相关规范(如建筑高度、消防通道、设备间距等),确保效果图符合实际要求。
技能要点:
熟悉工业建筑标准(如GB 50016-2014《建筑设计防火规范》)。
能够根据设计图纸调整模型细节,避免后期施工问题。
设备与工艺知识
核心要求:理解厂房内设备类型(如生产线、起重机、管道等)及其工艺流程,确保模型与实际一致。
技能要点:
掌握设备尺寸、安装位置及管线布局要求。
能够通过效果图展示设备运行逻辑(如物料流向、操作流程等)。
材料与工艺选择
核心要求:了解不同建筑材料的特性(如耐火性、防腐性、承重能力等),确保材质表现符合实际。
技能要点:
熟悉常见材料(如钢结构、混凝土、玻璃幕墙等)的渲染效果。
能够通过材质调整模拟不同工艺(如喷涂、氧化、镀膜等)。
五、沟通与协作能力
需求理解能力
核心要求:能够与客户、设计师、工程师等多方沟通,准确理解项目需求。
技能要点:
掌握需求分析方法,提炼关键信息。
能够通过草图、示意图等方式快速反馈设计思路。
团队协作能力
核心要求:在项目团队中与其他成员(如建筑师、结构工程师、施工团队等)紧密协作,确保效果图与实际施工一致。
技能要点:
熟悉项目流程,明确各阶段交付成果。
能够通过版本控制、注释标注等方式提升协作效率。
问题解决能力
核心要求:在制作过程中遇到技术难题(如渲染卡顿、模型穿插等)时,能够快速定位问题并解决。
技能要点:
掌握调试技巧,优化模型与渲染设置。
能够通过团队讨论或外部资源(如论坛、教程)寻求解决方案。
六、案例分析与实践能力
案例分析能力
核心要求:通过分析优秀厂房效果图案例,学习设计思路、技术实现与风格表现。
技能要点:
提取案例中的创新点(如材质组合、灯光设计、动线规划等)。
结合项目需求,灵活应用案例中的技术方法。
实践能力
核心要求:通过实际项目积累经验,提升制作效率与质量。
技能要点:
掌握项目时间管理技巧,确保按时交付。
能够通过客户反馈优化设计流程,提升客户满意度。
The production of factory renderings can be divided into the following categories based on different application scenarios, display focuses, and user needs, each of which has unique application value:
1、 Classified by application scenario
Project planning stage rendering
Core purpose: In the early stage of factory construction, it is used to showcase the overall planning layout, architectural style, and surrounding environmental relationships.
Characteristics: Emphasis on macro perspective, highlighting the coordination between the factory building and the surrounding terrain and transportation, providing intuitive reference for decision-makers.
Case: The design rendering of the factory cluster in the development zone should clearly present the functional zoning and logistics flow of each factory.
Investment Promotion Effect Diagram
Core purpose: To attract investors' attention, showcase the production environment, supporting facilities, and location advantages of the factory.
Characteristics: Emphasize the modernization level, space utilization rate, and surrounding industrial cluster effect of the factory building, and highlight the potential for investment return.
Case: Industrial park factory renderings, with key information such as transportation convenience and policy support marked.
Construction guidance rendering
Core purpose: To provide precise guidance for construction teams on building structures, equipment installation, and pipeline layout.
Characteristic: Pay attention to detail annotation, such as load-bearing structure, equipment foundation dimensions, and pipeline routing, which must strictly correspond to the construction drawings.
Case: A rendering of a heavy industrial plant that clearly indicates the installation location and lifting path of large equipment.
Corporate promotional effect picture
Core purpose: To enhance corporate image, showcase factory production capacity, technological innovation, and environmental protection concepts.
Characteristics: Highlighting the technological sense of the factory's exterior, the automation level of the internal production line, and environmental protection facilities, it is necessary to reflect the core competitiveness of the enterprise.
Case: A rendering of a factory building for an intelligent manufacturing enterprise, displaying scenes such as intelligent warehousing and robot production lines.
2、 Classify by display focus
Architectural exterior rendering
Core purpose: To showcase the architectural style, materials, and color matching of the factory building.
Characteristics: Emphasize the integration of building facade design, roof styling, and surrounding landscape, and reflect architectural aesthetics.
Case: Modern style factory renderings that highlight design elements such as glass curtain walls and metal lines.
Internal layout rendering
Core purpose: To showcase the interior space planning, equipment layout, and logistics flow of the factory building.
Characteristics: Emphasize the rationality of functional zoning, equipment placement efficiency, and personnel operation convenience, and reflect the optimization of production processes.
Case: The rendering of a food processing plant needs to clearly define functional zones such as production area, storage area, and inspection area.
Equipment installation rendering
Core purpose: To guide the installation location, foundation dimensions, and pipeline connections of large equipment.
Characteristics: Accurate annotation of equipment dimensions, installation height, and pipeline routing is required to ensure construction accuracy.
Case: The rendering of a chemical equipment factory needs to clarify the installation positions and connection methods of equipment such as reaction vessels and pipelines.
3、 Classify according to user needs
Government approval requirement rendering
Core purpose: To meet the approval requirements of government planning departments for factory construction.
Characteristics: It needs to comply with relevant specifications and standards, such as building height, plot ratio, greening rate, etc., and detailed technical parameters need to be provided.
Case: The factory planning rendering submitted to the Housing and Urban Rural Development Bureau needs to indicate key information such as building red lines and setback distances.
Customer customized requirement rendering
Core purpose: Customize factory design solutions based on personalized customer needs.
Characteristics: It is necessary to fully communicate with customers about their production processes, equipment types, and special needs, and provide customized solutions.
Case: A customized factory rendering for a new energy enterprise that meets the special environmental requirements of the battery production line.
Investment analysis demand rendering
Core purpose: To provide investors with a basis for analyzing the economic benefits of factory construction.
Characteristics: It is necessary to display the construction cost, operating cost, and expected revenue of the factory building, and to conduct financial model calculations.
Case: The factory rendering provided to investment institutions should include key indicators such as investment return rate and payback period.
As an important tool for showcasing factory design schemes, planning layouts, and future appearances, factory renderings have the following significant advantages:
1、 Visually display design results
3D rendering: Factory renderings use 3D modeling technology to present the appearance, internal structure, equipment layout, and other aspects of the factory in a three-dimensional form, allowing decision-makers, investors, and design teams to visually see the design results without the need for complex textual descriptions or 2D drawings.
Clear and visible details: The rendering can finely present various details of the factory, such as the material and color of the building exterior, the model and location of internal equipment, and the layout of the production line, providing comprehensive information support for decision-makers.
2、 Easy to communicate and make decisions
Facilitating multi-party communication: Factory renderings provide a common communication platform for designers, engineers, investors, and management to engage in in-depth discussions on design proposals, identify problems in a timely manner, and make adjustments and optimizations.
Assisted decision-making: Through renderings, decision-makers can more intuitively evaluate the feasibility and economy of design schemes, thereby making wiser decisions.
3、 Optimize design scheme
Identifying potential issues in advance: During the rendering process, designers can simulate the actual operation of the factory, identify potential problems in the design in advance, such as unreasonable spatial layout, equipment conflicts, etc., and make timely adjustments.
Optimize resource allocation: Through renderings, the factory's resource allocation can be more clearly planned, such as personnel flow routes, material transportation routes, etc., to improve production efficiency and reduce operating costs.
4、 Enhance project attractiveness
Enhancing project credibility: Professional factory renderings can showcase the professionalism and feasibility of the project, boosting the confidence of investors and partners in the project.
Attracting potential customers: For enterprises that need to showcase the strength of their factories, renderings are an effective promotional tool that can attract the attention of potential customers and promote business cooperation.
5、 Support construction planning and guidance
Clear construction requirements: The rendering provides clear construction guidance for the construction team, including building structure, equipment installation location, pipeline layout, etc., which helps the construction team to more accurately understand the design intent and reduce misunderstandings and errors during the construction process.
Optimize construction process: Through renderings, the construction team can plan the construction process in advance, arrange the construction sequence reasonably, improve construction efficiency, and shorten the construction period.
The production of factory renderings is a comprehensive technical task that involves skills and knowledge from multiple fields. The following are the main skills required to create factory renderings:
1、 Basic skills
3D modeling capability
Core requirement: Proficient in 3D modeling software (such as 3ds Max, Maya, SketchUp, etc.), able to create 3D models of factories based on design drawings or sketches.
Key Skills:
Familiar with techniques such as polygon modeling and surface modeling.
Can accurately restore the architectural structure, equipment layout, and detailed features of the factory building.
Master model optimization techniques to ensure rendering efficiency.
Materials and Texture Applications
Core requirement: Understand the physical properties of different materials (such as metal, concrete, glass, etc.) and be able to simulate real effects through a material editor.
Key Skills:
Master UV unfolding technology to ensure accurate mapping of texture maps.
Familiar with PBR (physics based rendering) material process to enhance material realism.
Lighting and rendering technology
Core requirement: Master the principles of lighting layout and be able to simulate natural light, artificial light, and ambient light effects.
Key Skills:
Familiar with global lighting, HDRI environment mapping and other technologies.
Master the use of renderers such as V-Ray, Corona, Arnold, etc., and optimize rendering parameters.
Capable of balancing rendering quality and efficiency to meet project requirements.
2、 Design skills
Ability in spatial planning and layout
Core requirement: Understand the functional zoning of the factory building (such as production area, storage area, office area, etc.) and be able to plan the spatial flow reasonably.
Key Skills:
Master the principles of ergonomics, optimize personnel operations and equipment layout.
Familiar with logistics flow line design to improve production efficiency.
Color and Aesthetic Design
Core requirement: Ability to match colors and enhance the visual effect of the factory through color matching.
Key Skills:
Understand color psychology and choose color schemes that match the functionality of the factory building.
Master the contrast of light and shadow and visual focus design to enhance the sense of hierarchy in the picture.
Stylistic design ability
Core requirement: Adjust the design style according to the type of factory building (such as industrial style, modern style, technological style, etc.).
Key Skills:
Familiar with the architectural features and material expressions of different styles.
Can enhance stylized effects through post-processing, such as color tone adjustment, light and shadow enhancement, etc.
3、 Software skills
3D modeling software
Mainstream tools: 3ds Max, Maya, SketchUp, Rhino, etc.
Skill requirements:
Proficient in basic functions such as modeling, materials, lighting, etc.
Efficiency can be improved through plugins such as Forest Pack, RailClone, etc.
Rendering software
Mainstream tools: V-Ray, Corona, Arnold, Lumion, etc.
Skill requirements:
Master rendering parameter optimization techniques, balance quality and speed.
Familiar with post-processing processes such as Photoshop color grading, compositing, etc.
Auxiliary tools
CAD software: AutoCAD is used to read design drawings and ensure modeling accuracy.
Image processing software: Photoshop is used for post production color grading, compositing, and detail optimization.
Animation software: To create dynamic effects, you need to master tools such as After Effects and Premiere.
4、 Industry knowledge
Factory Design Specification
Core requirement: Understand the relevant regulations for factory construction (such as building height, fire exits, equipment spacing, etc.), and ensure that the rendering meets actual requirements.
Key Skills:
Familiar with industrial building standards (such as GB 50016-2014 "Code for Fire Protection Design of Buildings").
Being able to adjust model details based on design drawings to avoid construction issues in the later stages.
Equipment and process knowledge
Core requirement: Understand the types of equipment in the factory (such as production lines, cranes, pipelines, etc.) and their process flow, ensuring that the model is consistent with the actual situation.
Key Skills:
Master the requirements for equipment size, installation location, and pipeline layout.
Ability to display equipment operation logic (such as material flow, operation process, etc.) through renderings.
Material and process selection
Core requirement: Understand the characteristics of different building materials (such as fire resistance, corrosion resistance, load-bearing capacity, etc.) to ensure that the material performance is in line with reality.
Key Skills:
Familiar with rendering effects of common materials such as steel structures, concrete, glass curtain walls, etc.
Ability to simulate different processes (such as spraying, oxidation, coating, etc.) through material adjustment.
5、 Communication and collaboration skills
Ability to understand requirements
Core requirement: Able to communicate with clients, designers, engineers, and other parties to accurately understand project requirements.
Key Skills:
Master the methods of requirement analysis and extract key information.
Can quickly provide feedback on design ideas through sketches, diagrams, and other means.
Teamwork ability
Core requirement: Work closely with other members of the project team (such as architects, structural engineers, construction teams, etc.) to ensure that the renderings are consistent with the actual construction.
Key Skills:
Familiarize oneself with the project process and clarify the deliverables for each stage.
Ability to improve collaboration efficiency through version control, annotation, and other methods.
Problem solving ability
Core requirement: When encountering technical difficulties during the production process (such as rendering lag, model interweaving, etc.), be able to quickly locate and solve the problem.
Key Skills:
Master debugging skills, optimize models and rendering settings.
Ability to seek solutions through team discussions or external resources such as forums and tutorials.
6、 Case analysis and practical skills
Case analysis ability
Core requirement: By analyzing excellent factory rendering cases, learn design ideas, technical implementation, and style expression.
Key Skills:
Extract innovative points from the case (such as material combination, lighting design, flow planning, etc.).
Flexibly apply the technical methods in the case study based on project requirements.
Practical ability
Core requirement: Accumulate experience through practical projects to improve production efficiency and quality.
Key Skills:
Master project time management skills to ensure timely delivery.
Being able to optimize the design process and improve customer satisfaction through customer feedback.

 QQ咨询
QQ咨询
 189 5158 0154
189 5158 0154
 在线留言
在线留言

