下拉有很多__【询价/阅新品 + 右侧联系】
3d渲染图制作案例:
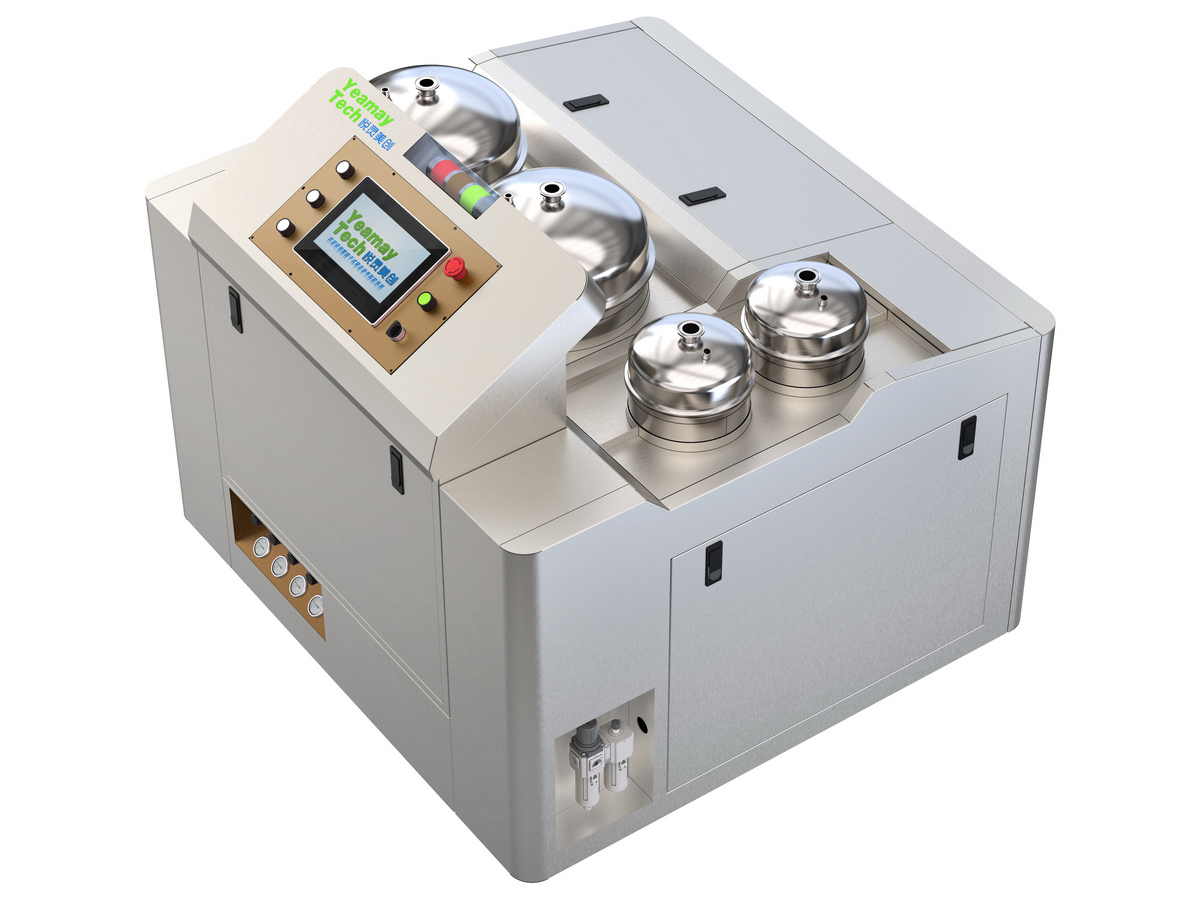
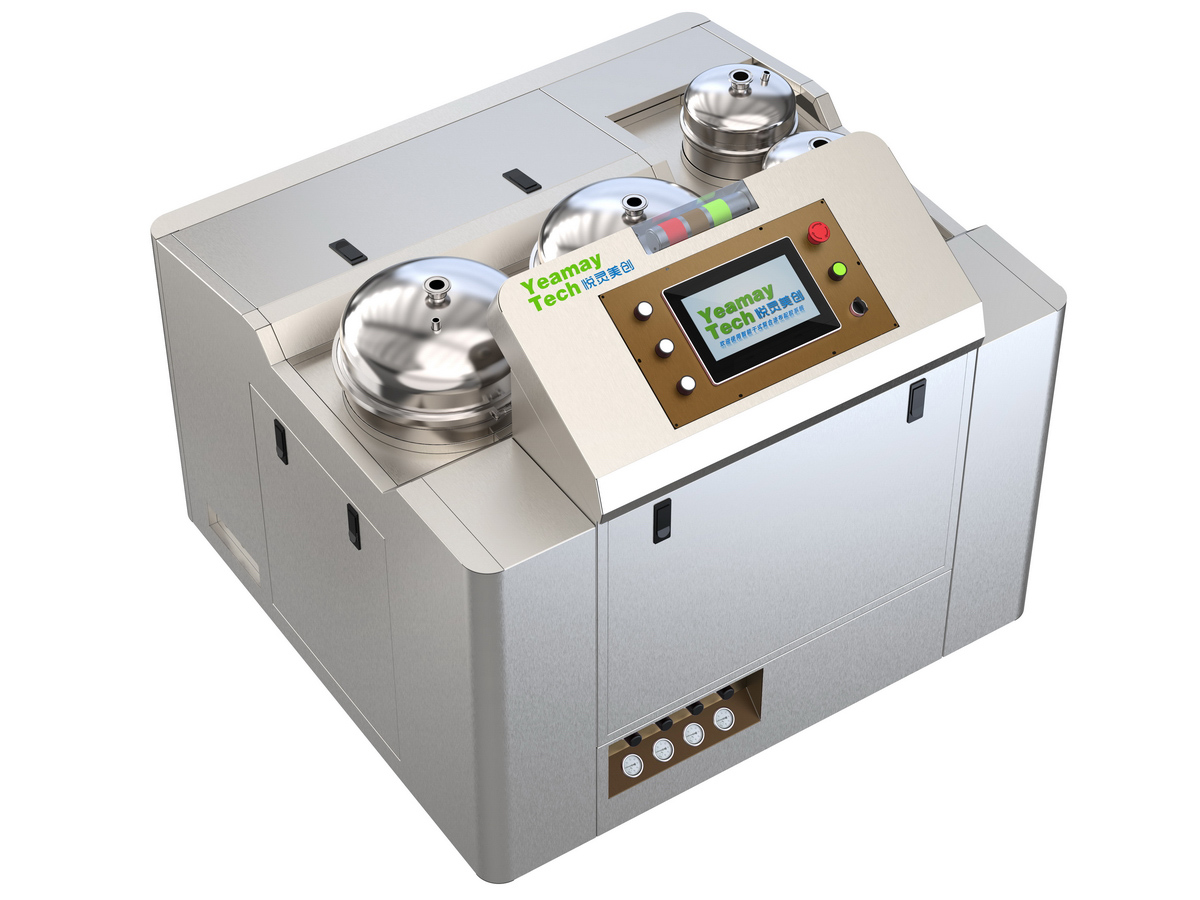
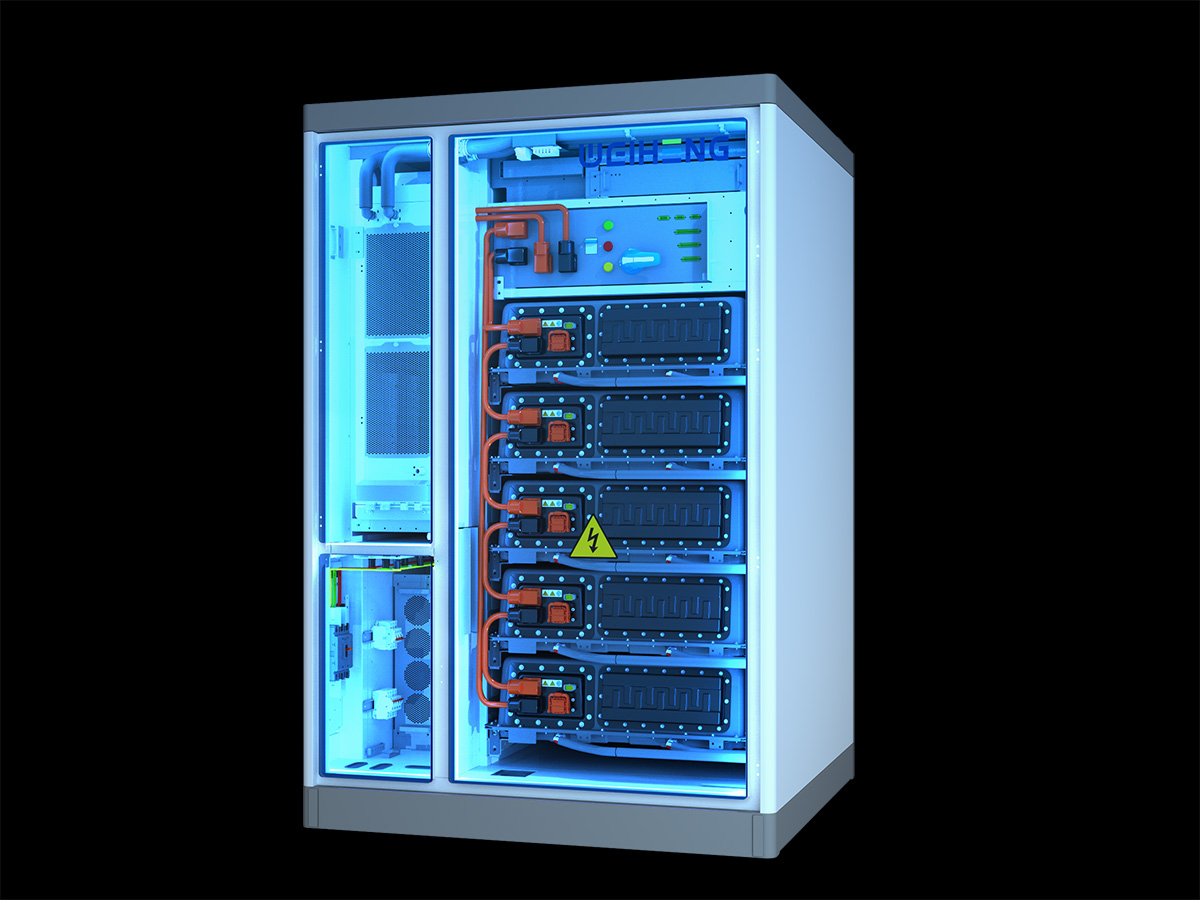
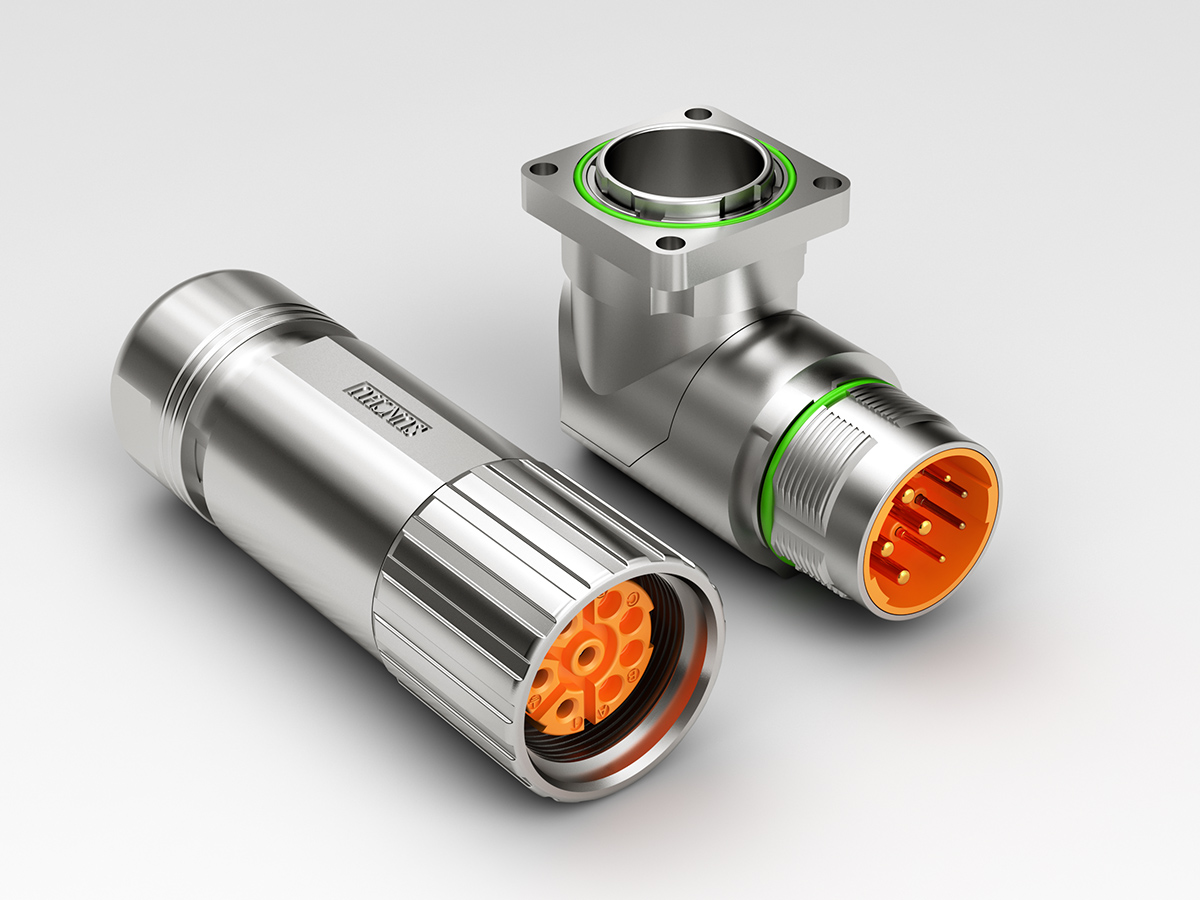
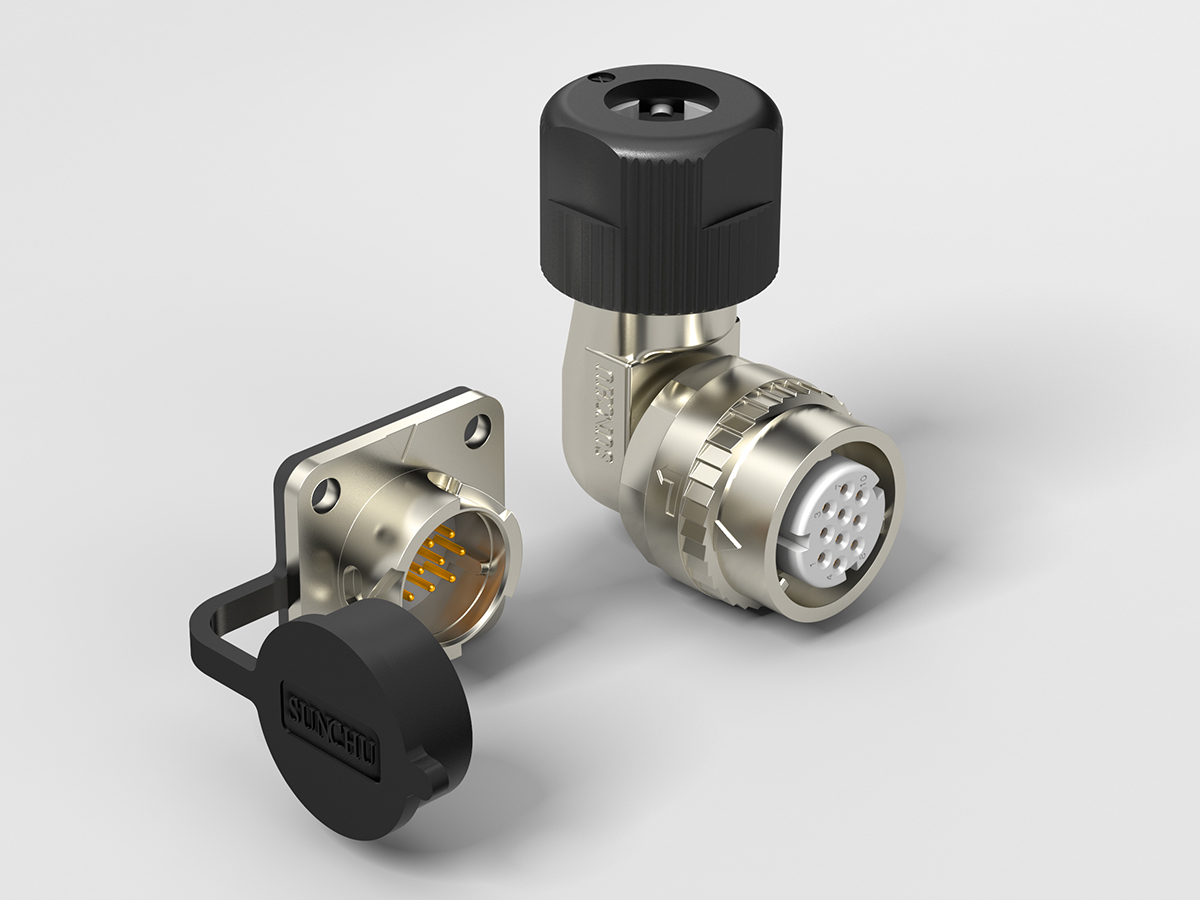
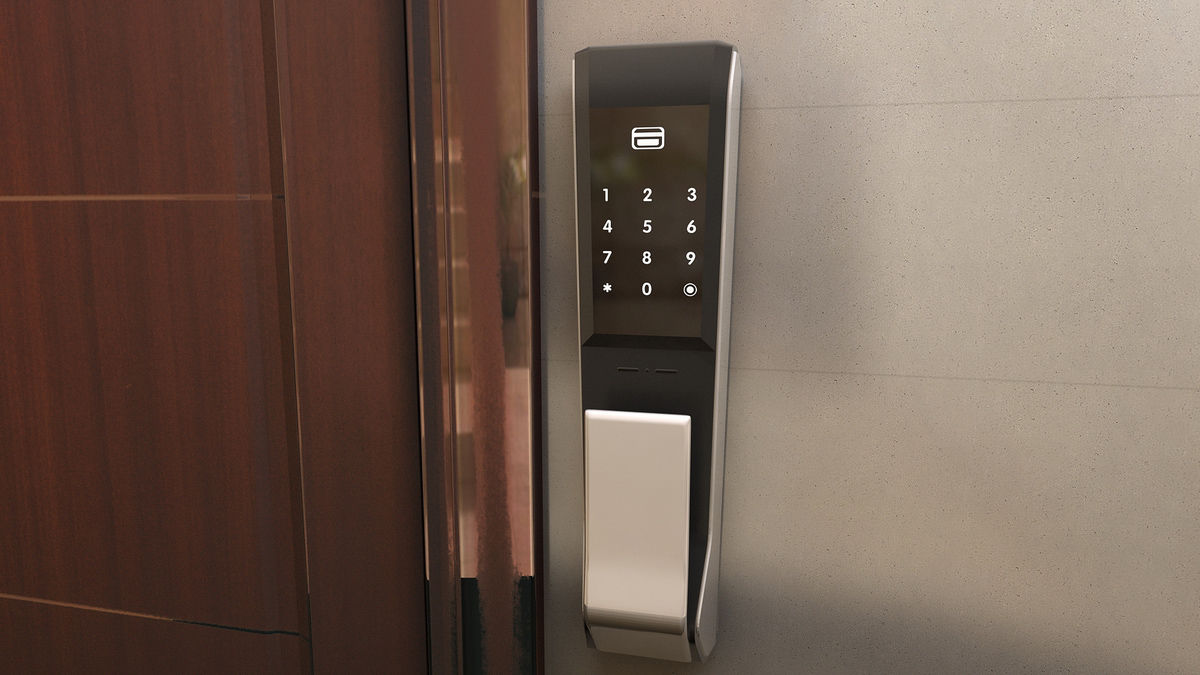
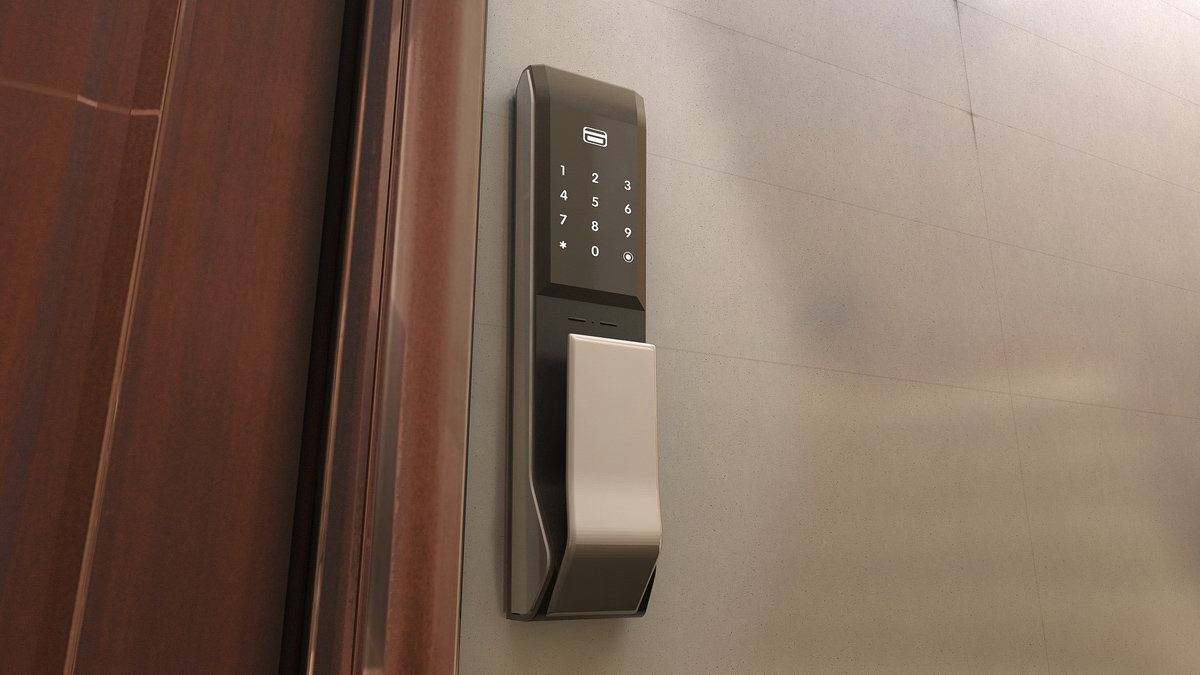
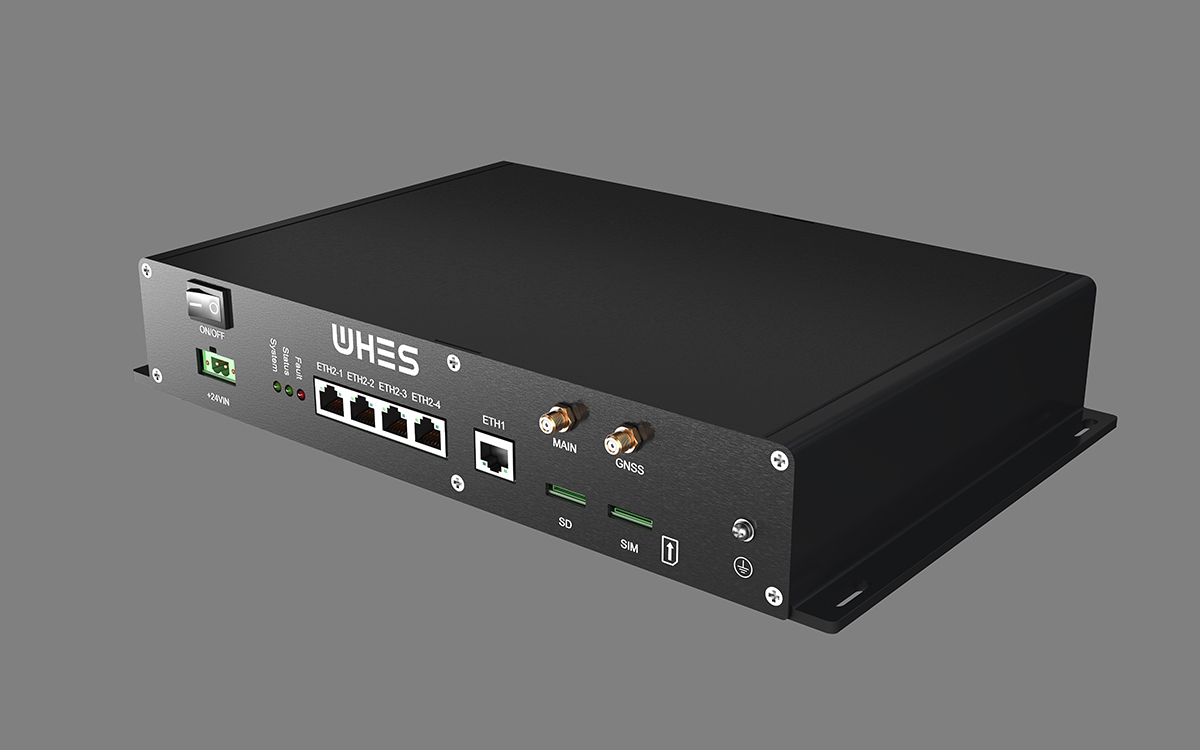
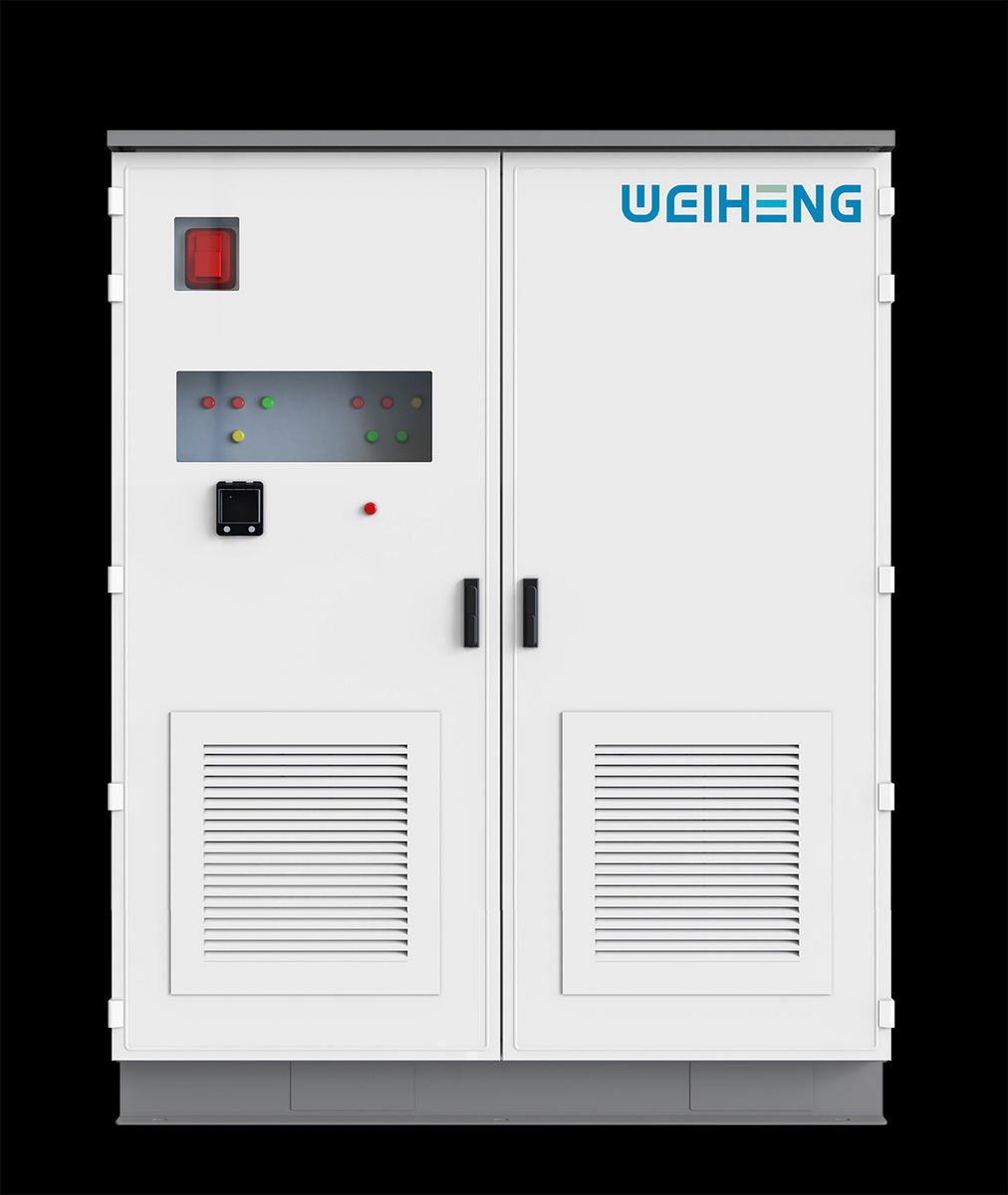
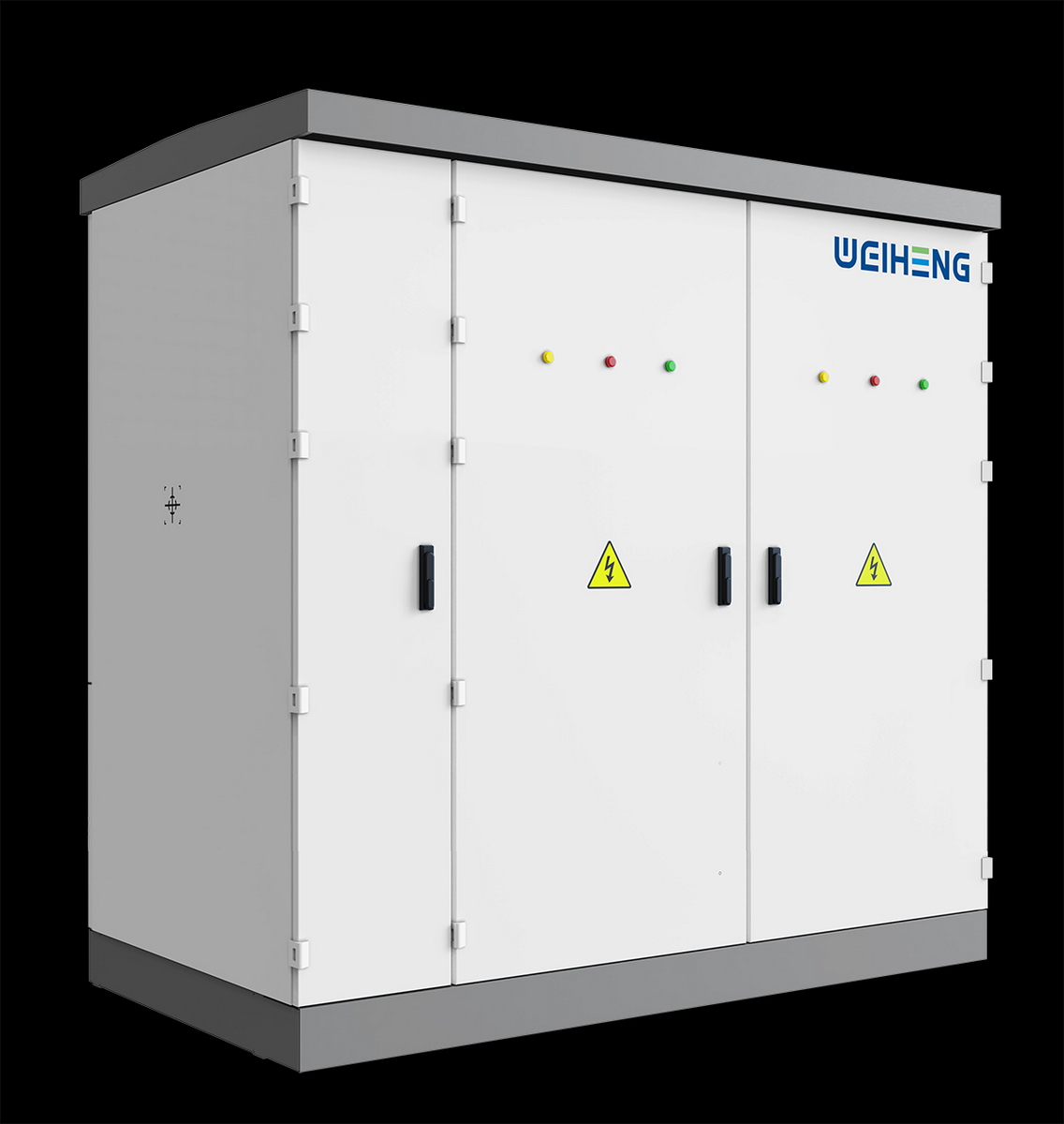
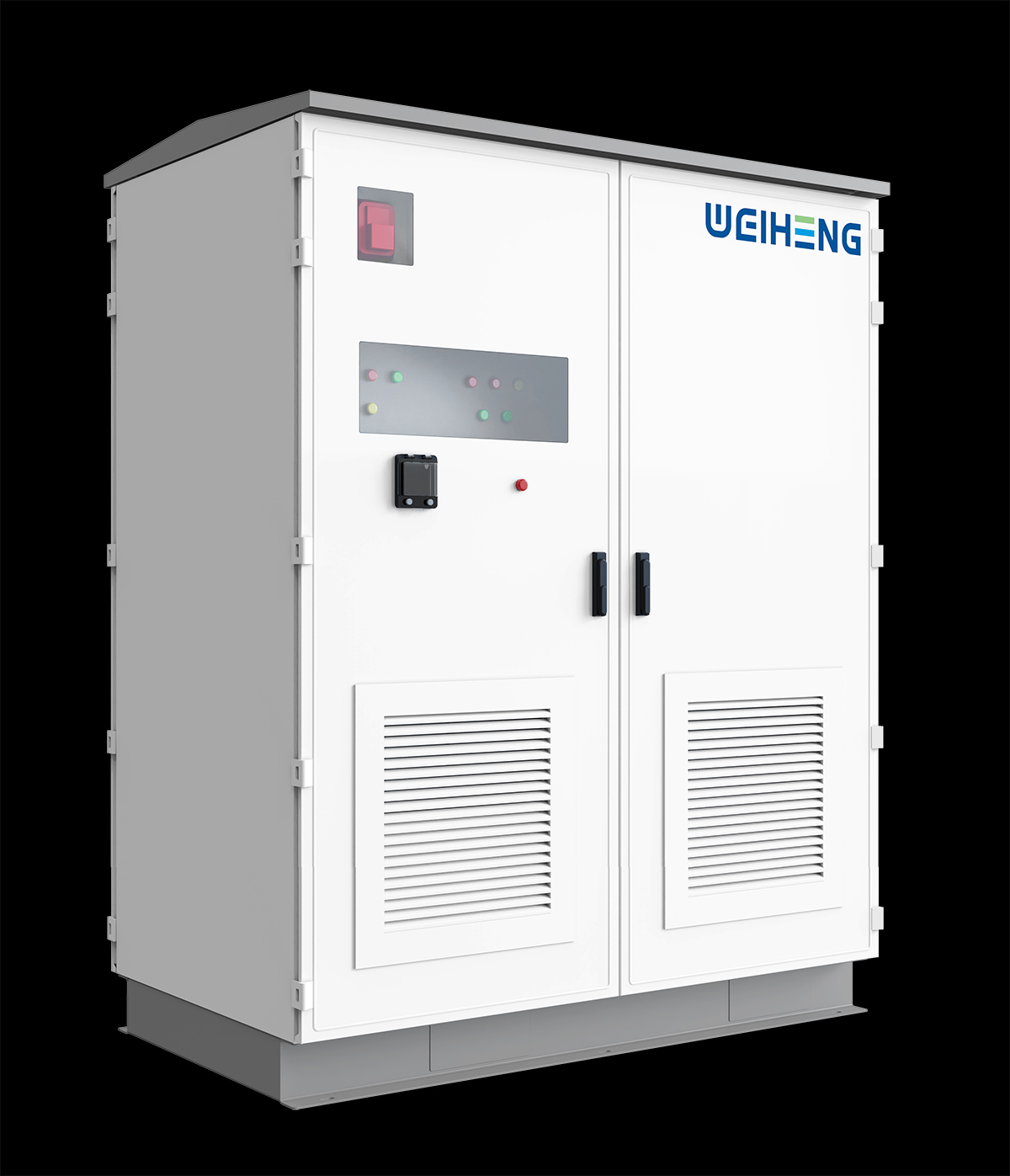
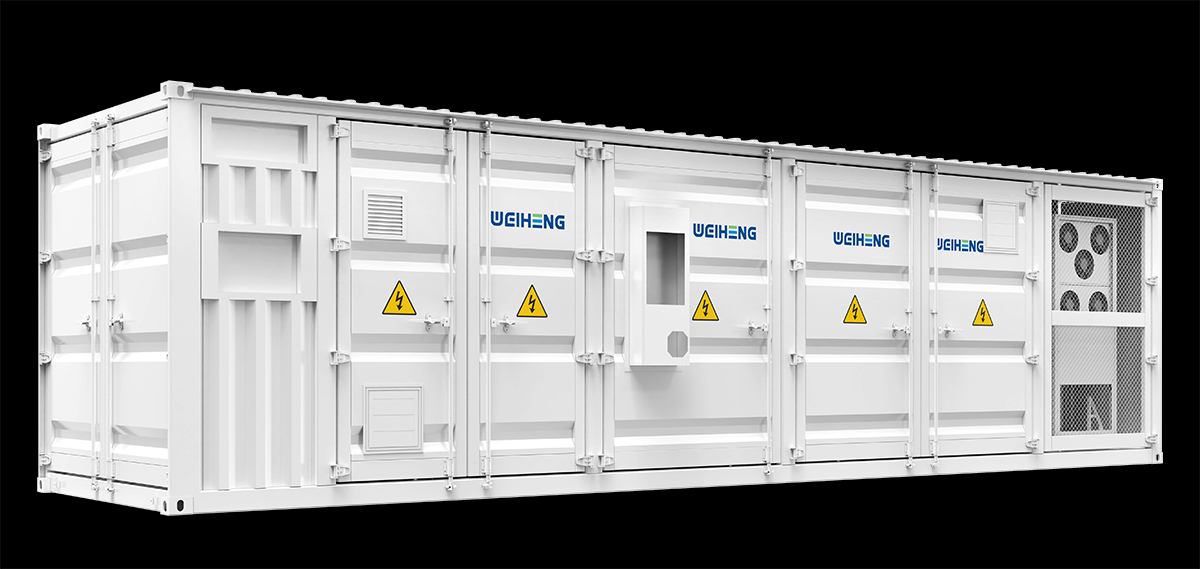
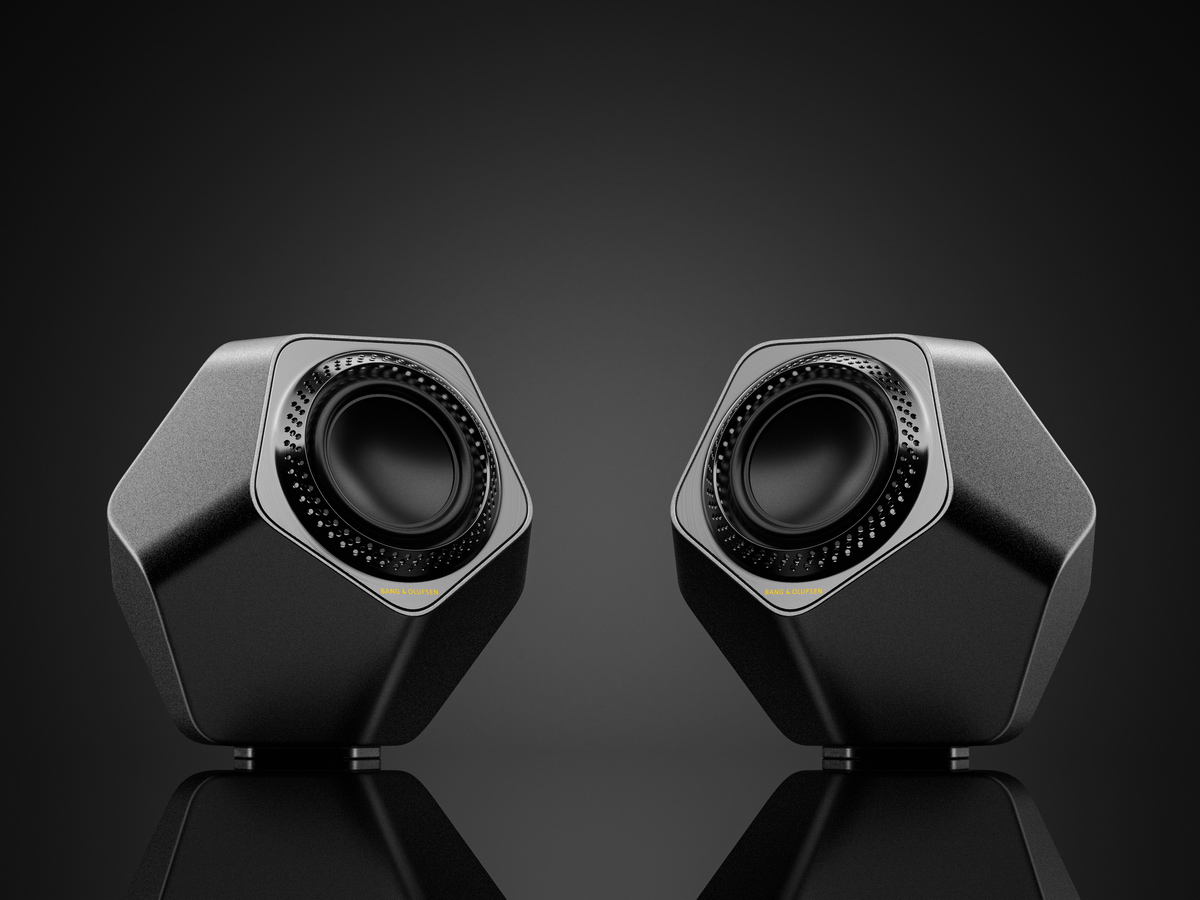
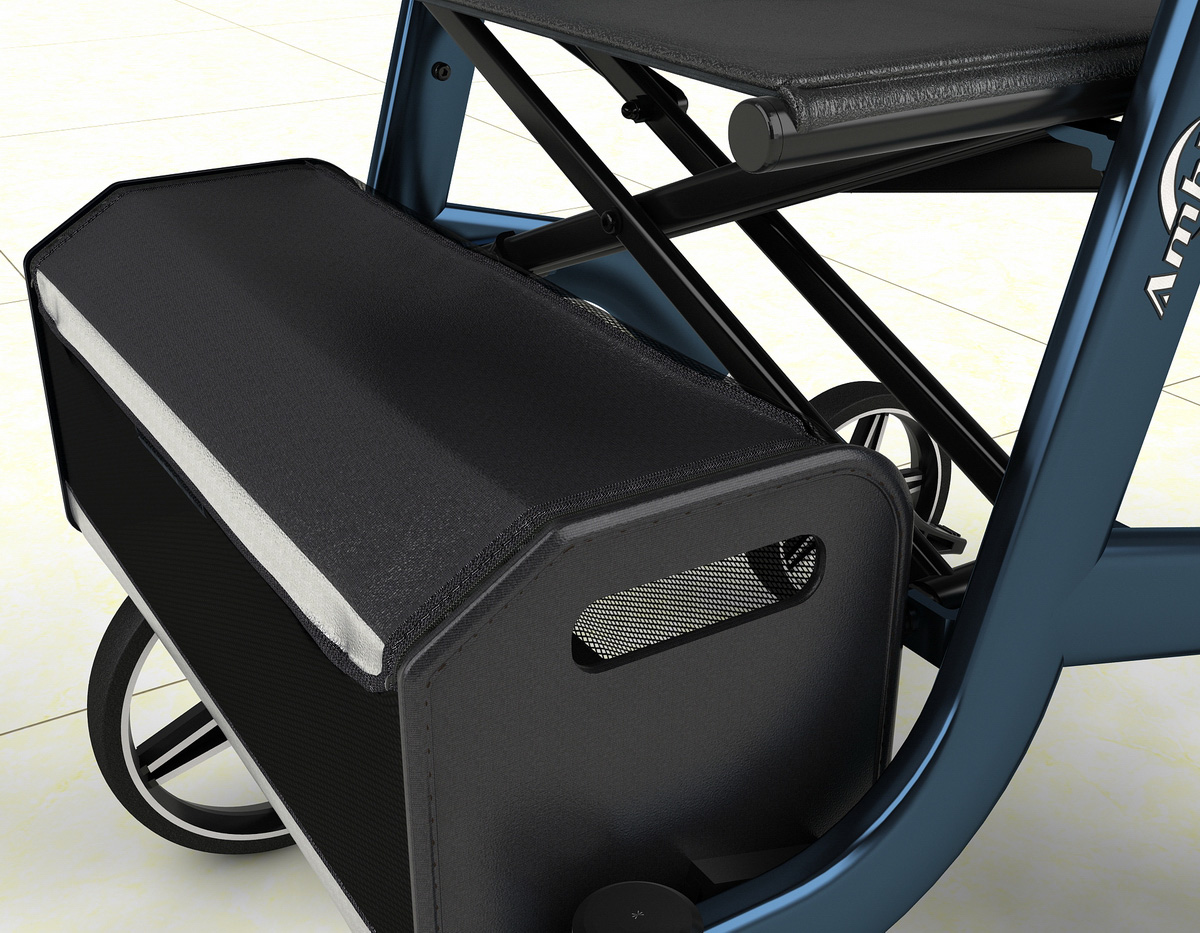
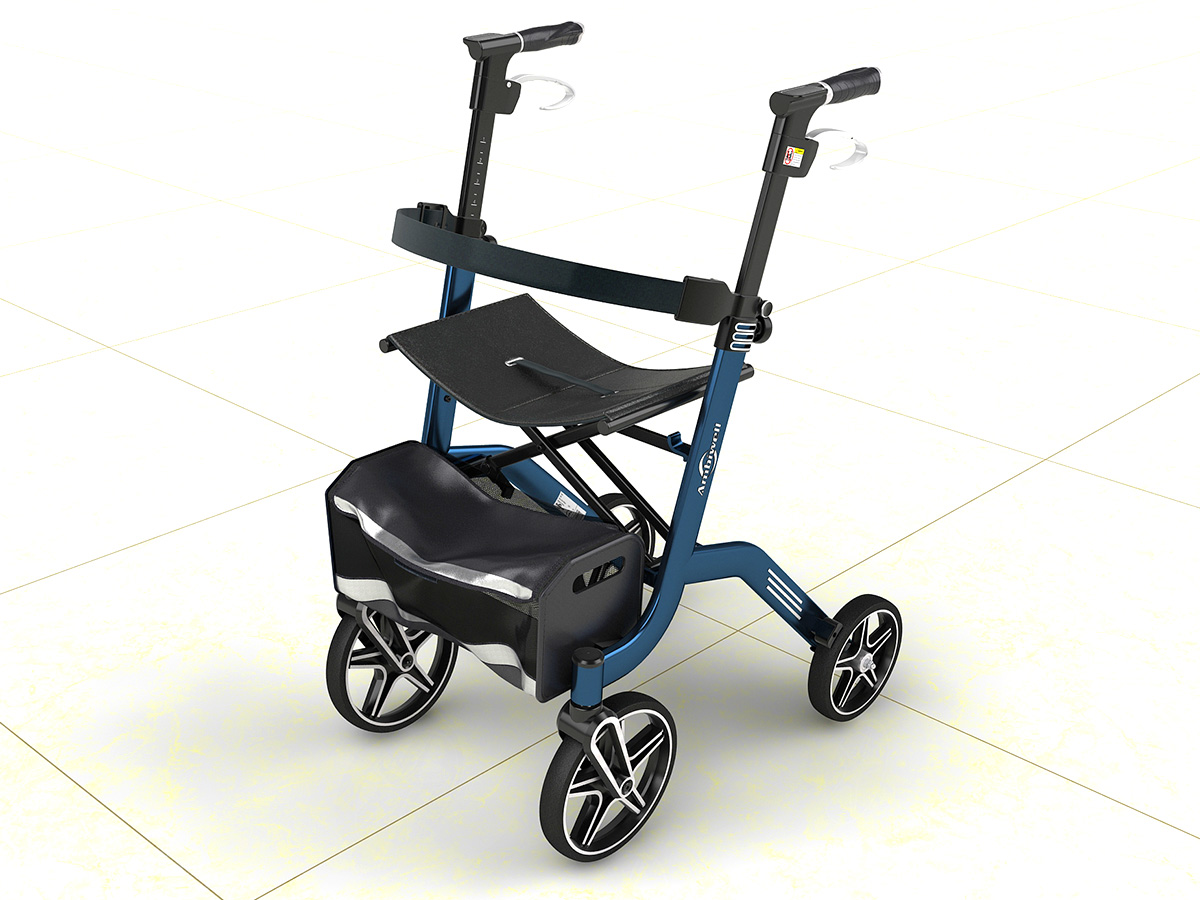
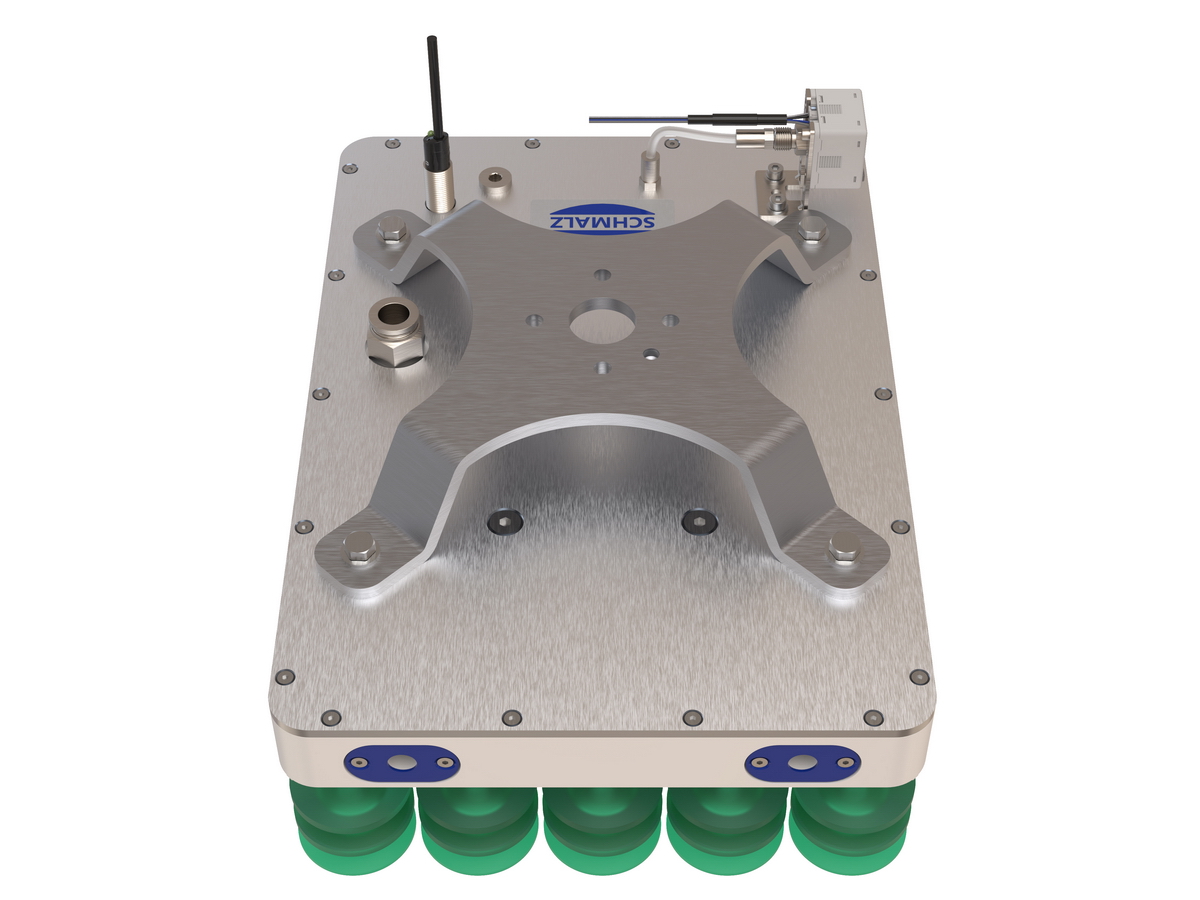
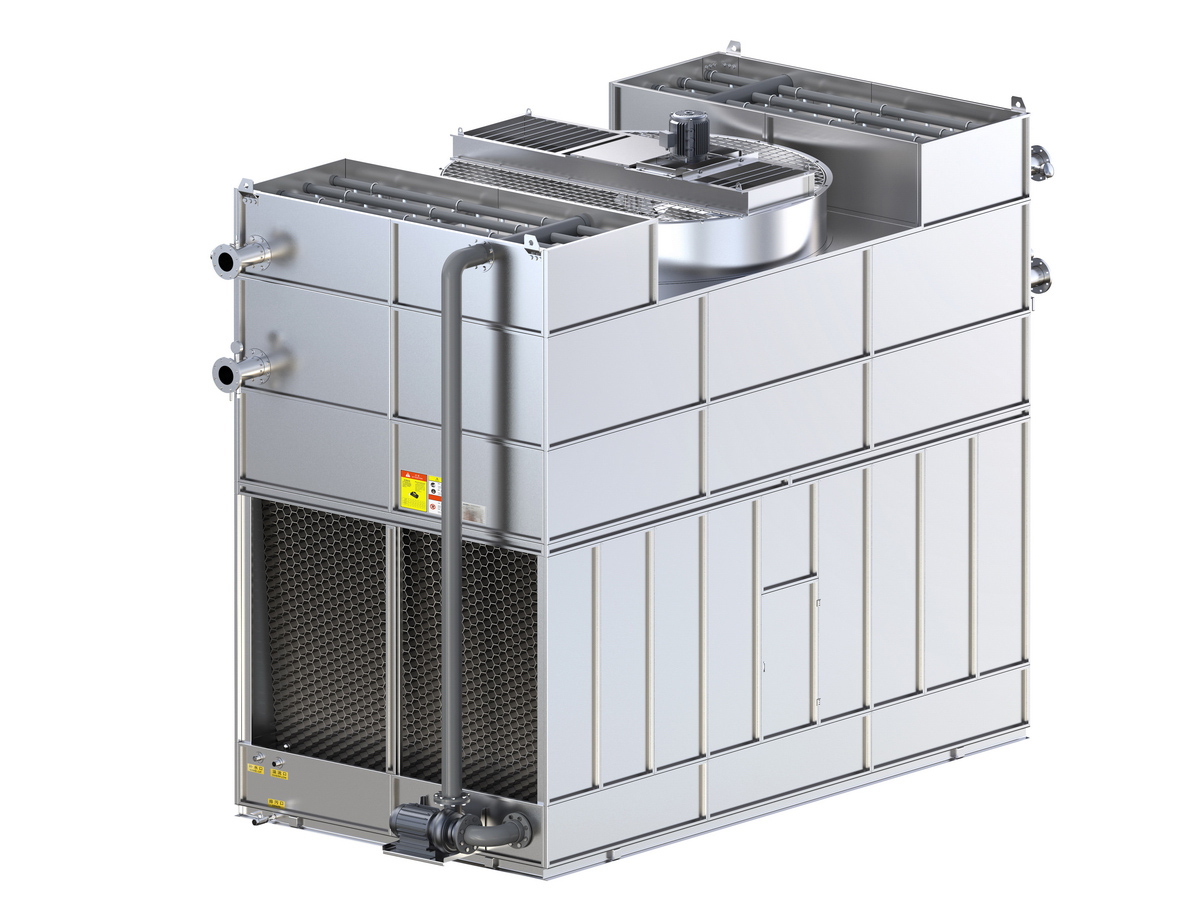
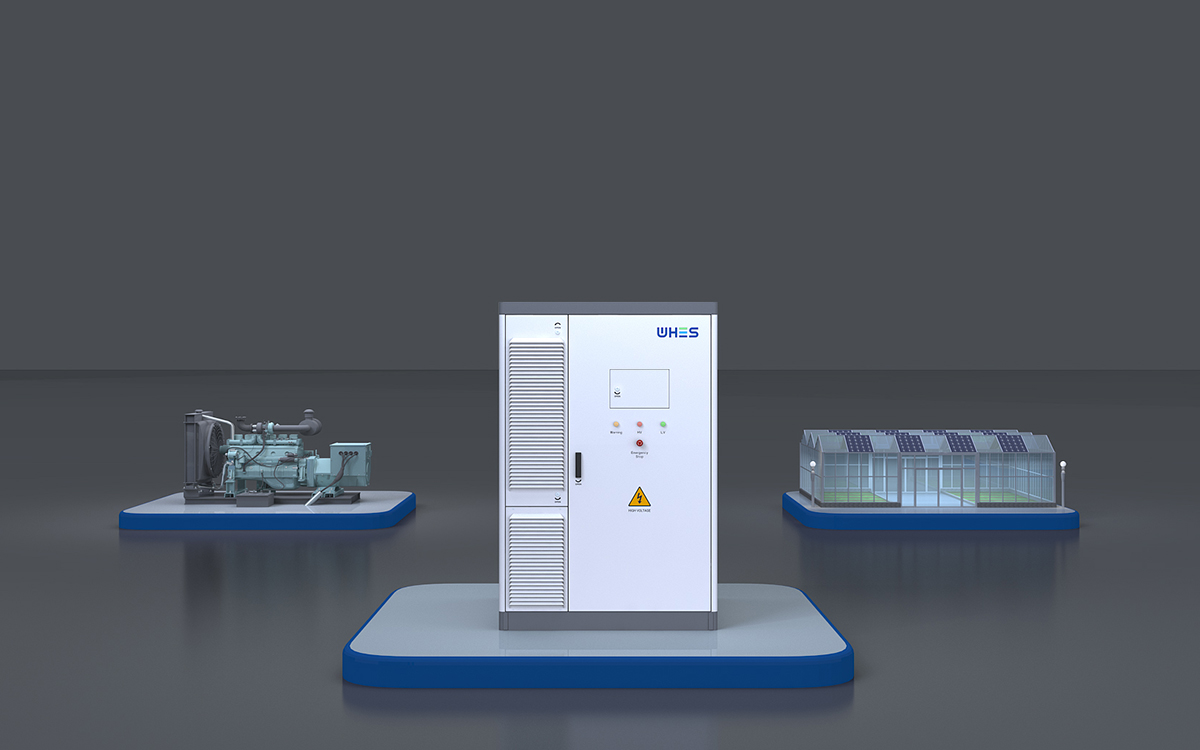


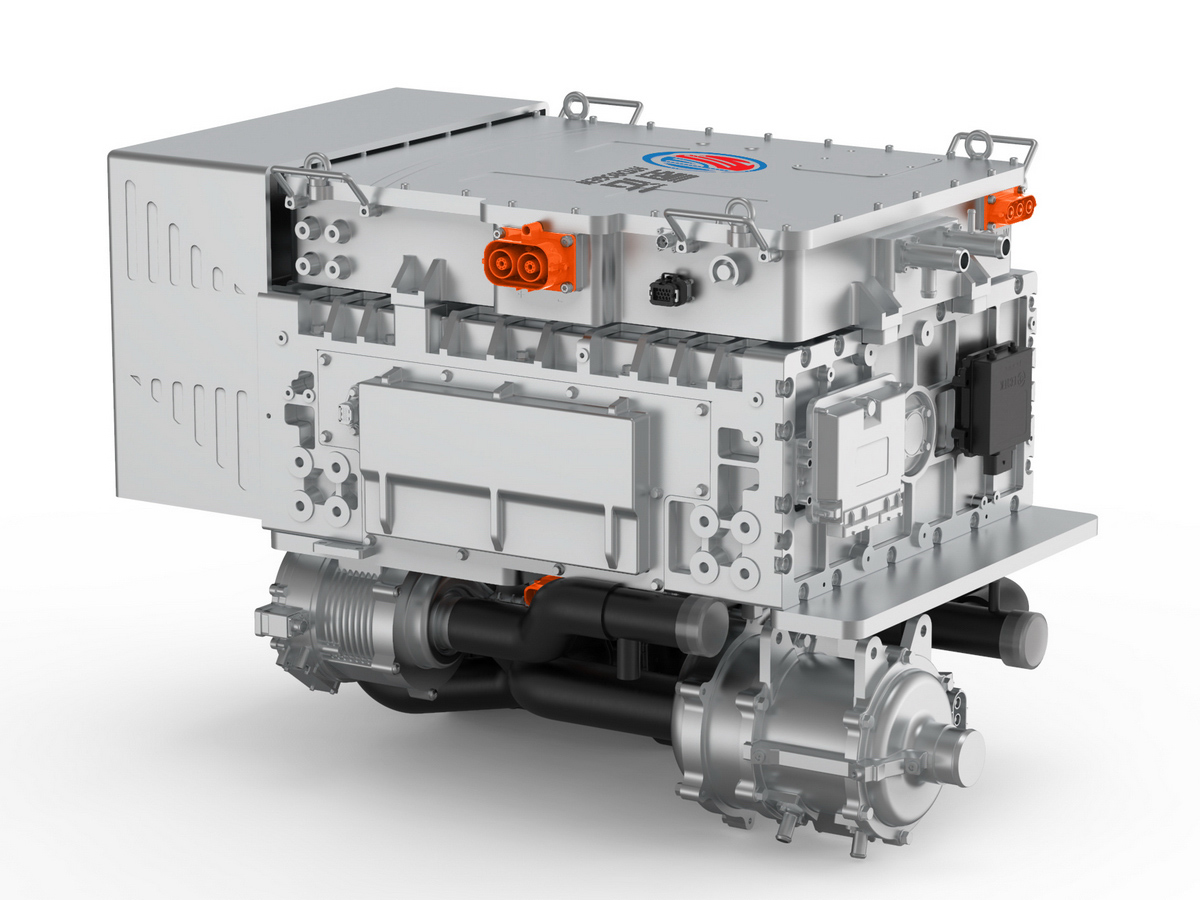
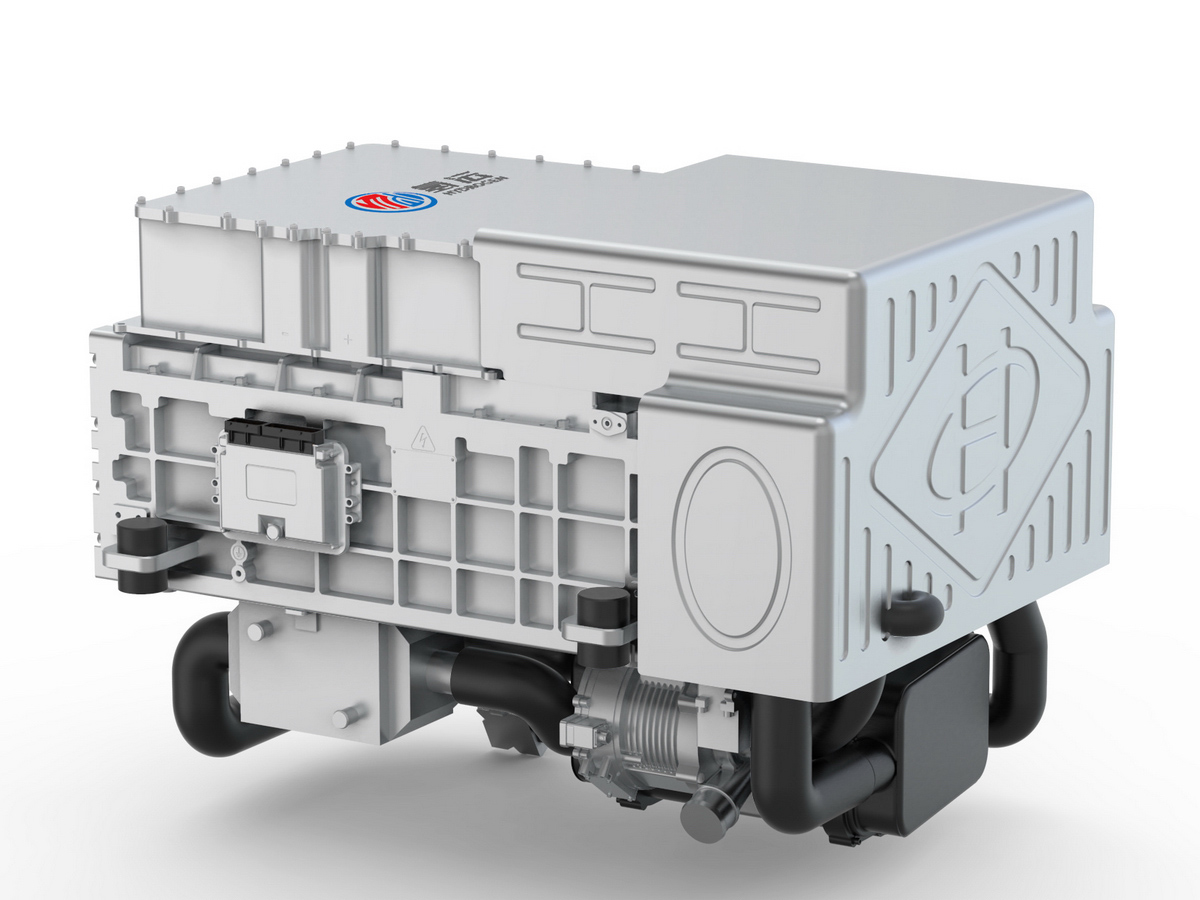
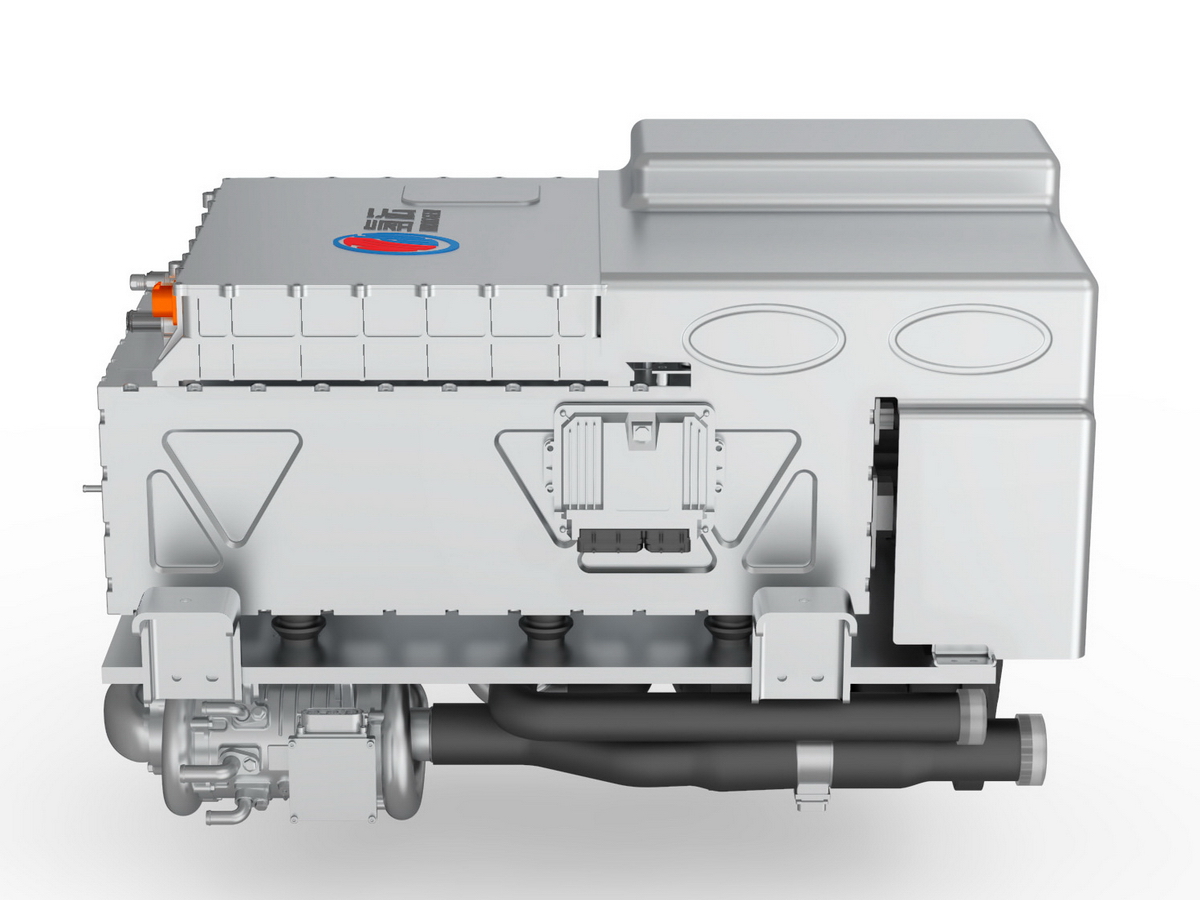
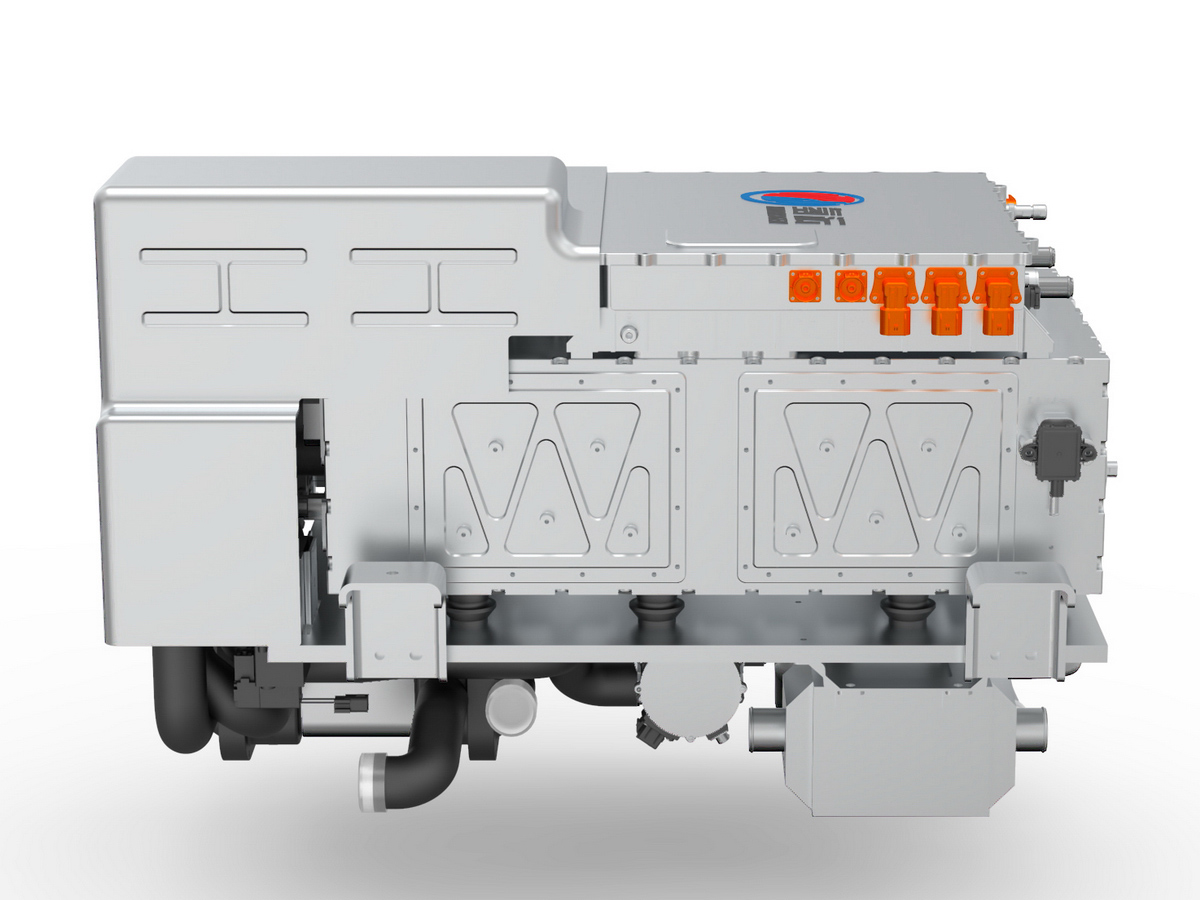
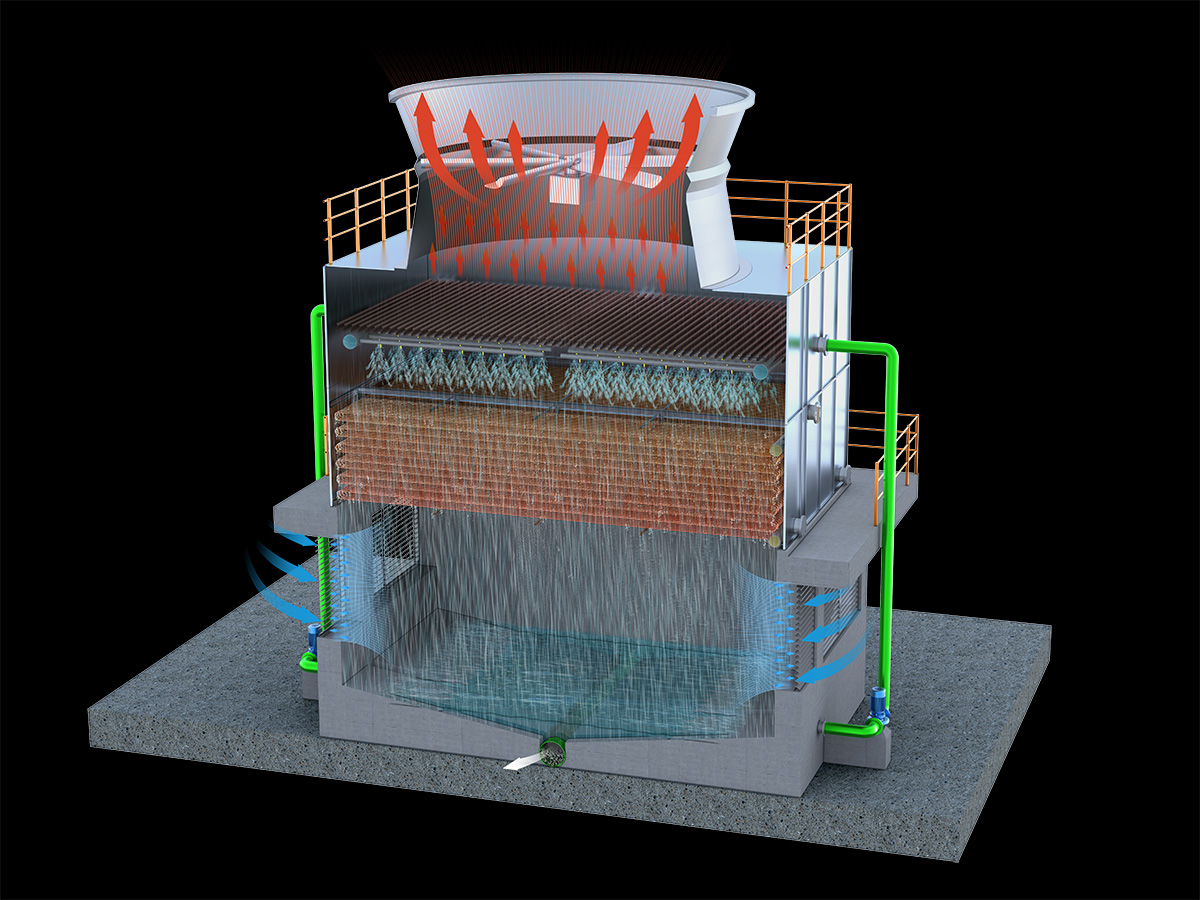








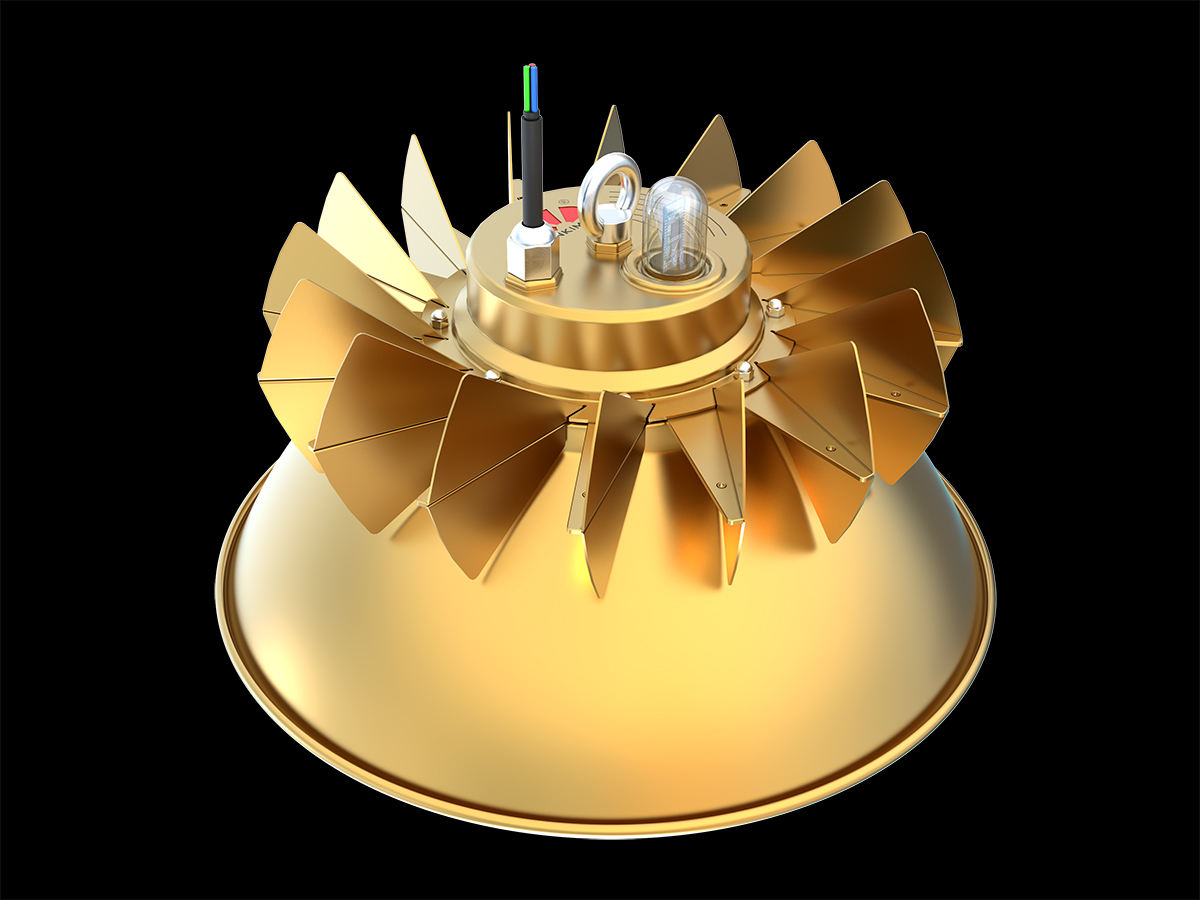
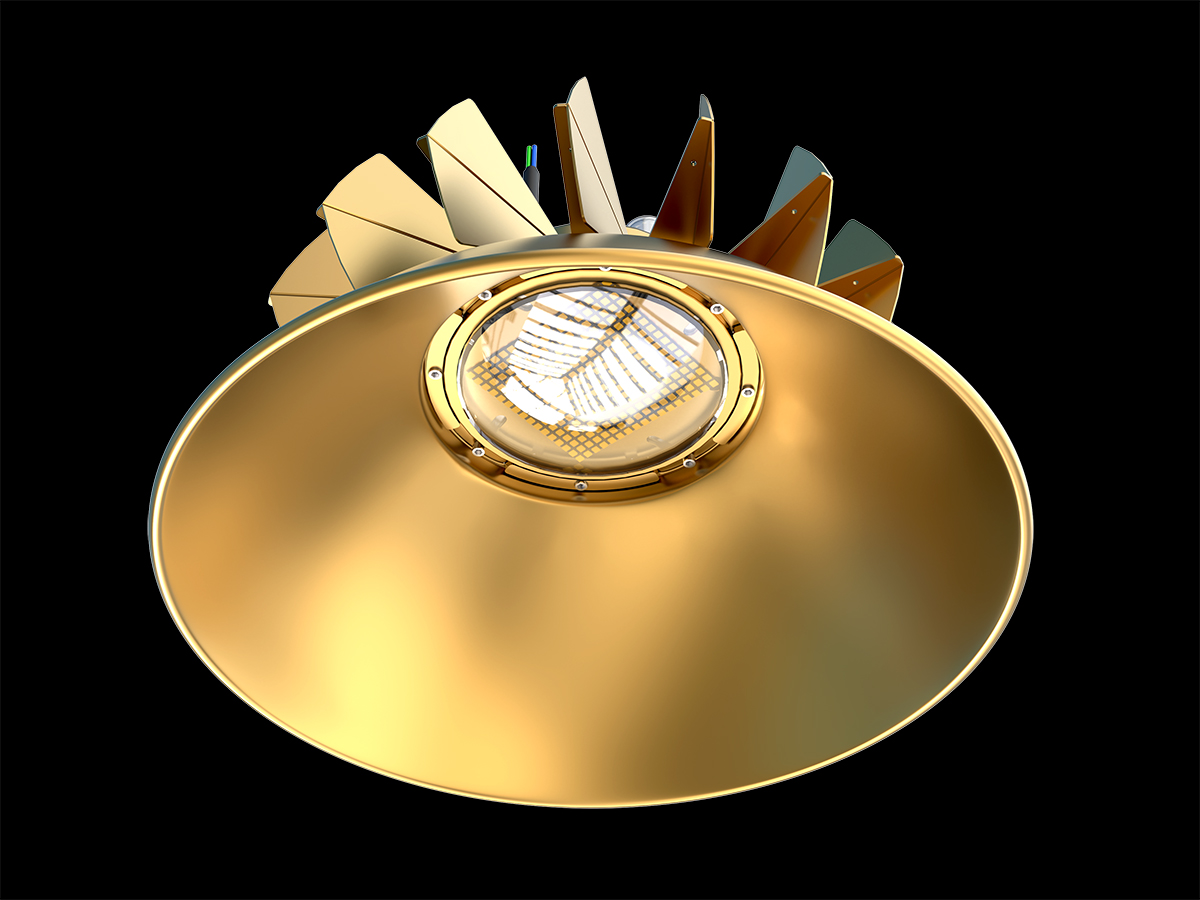


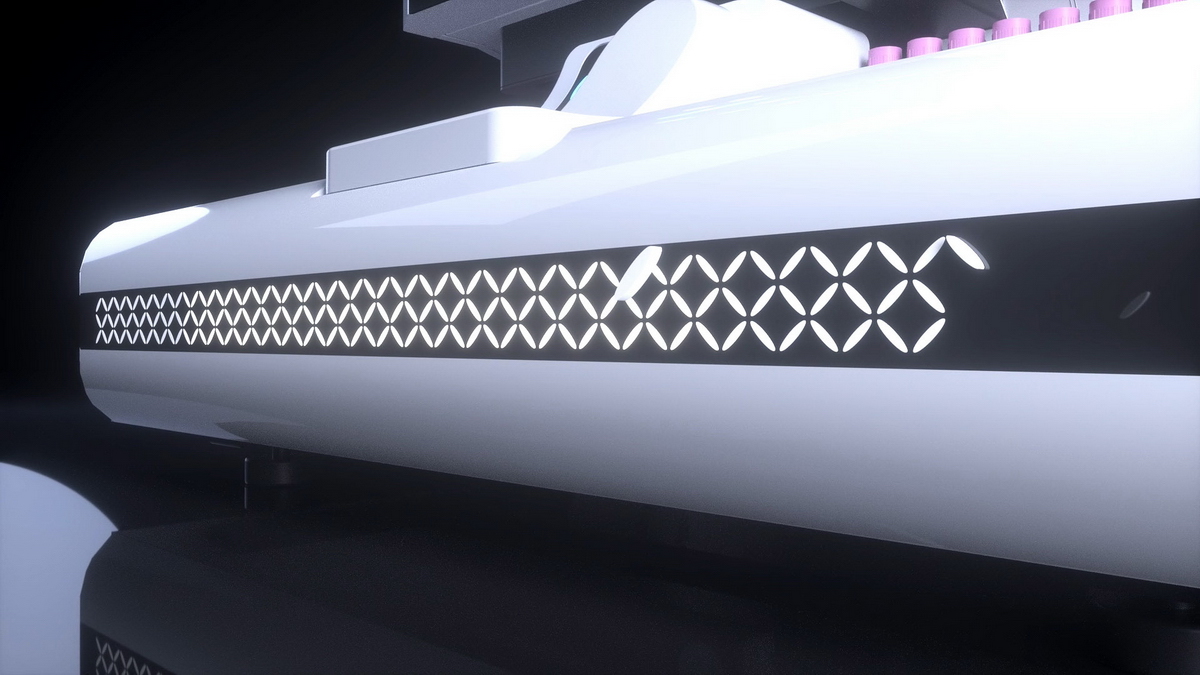









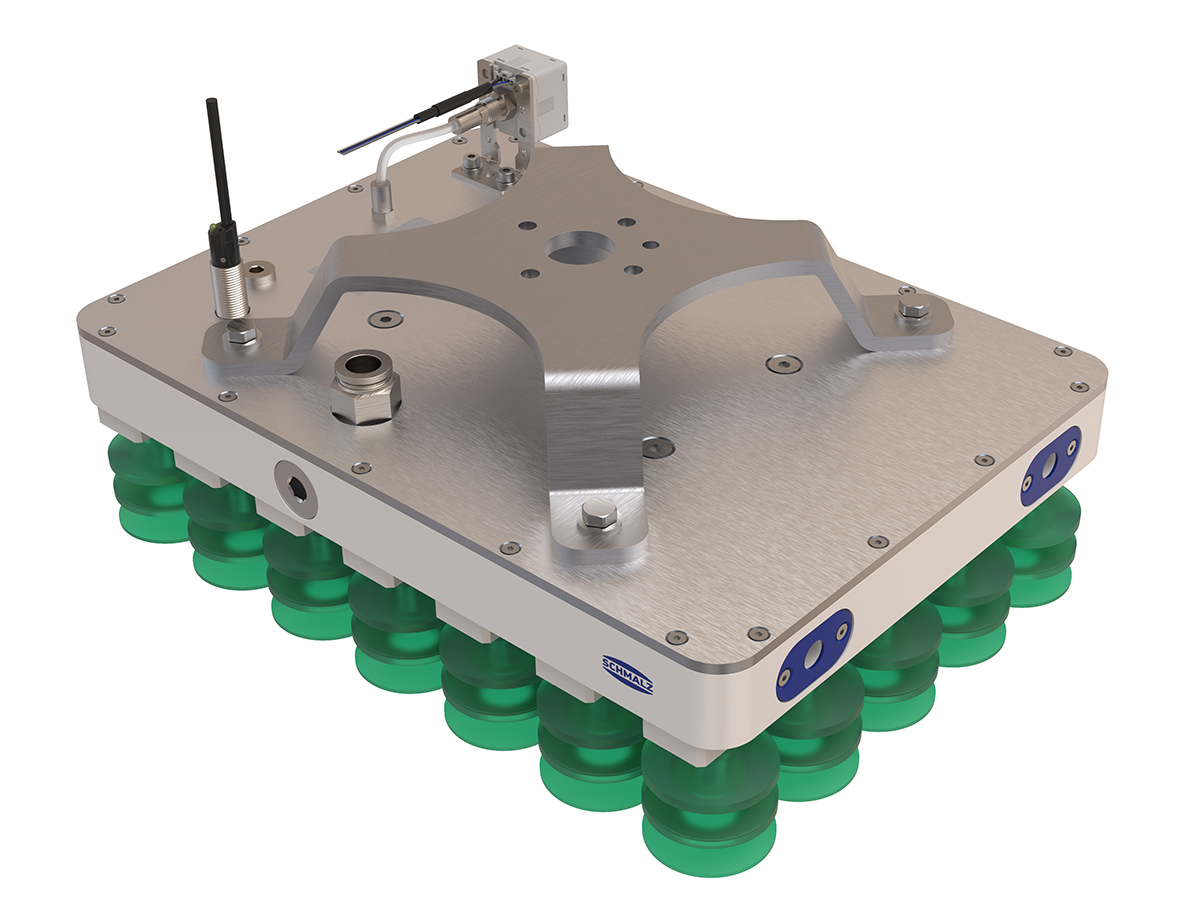
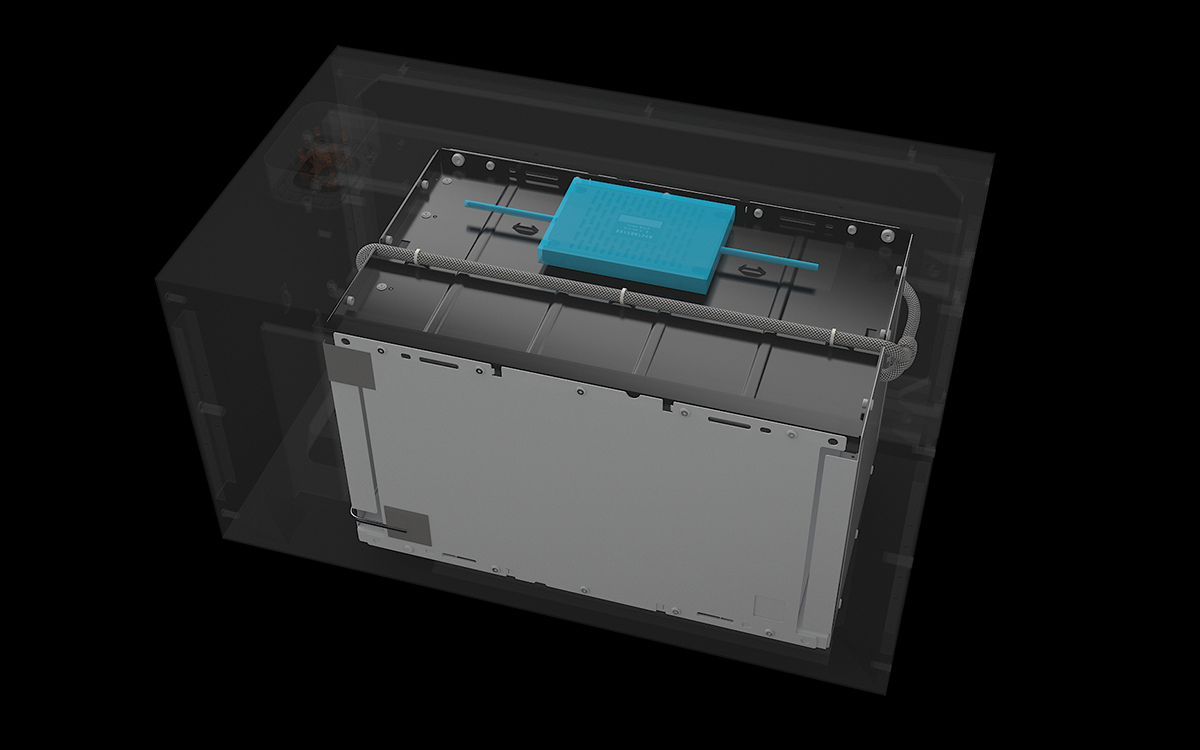

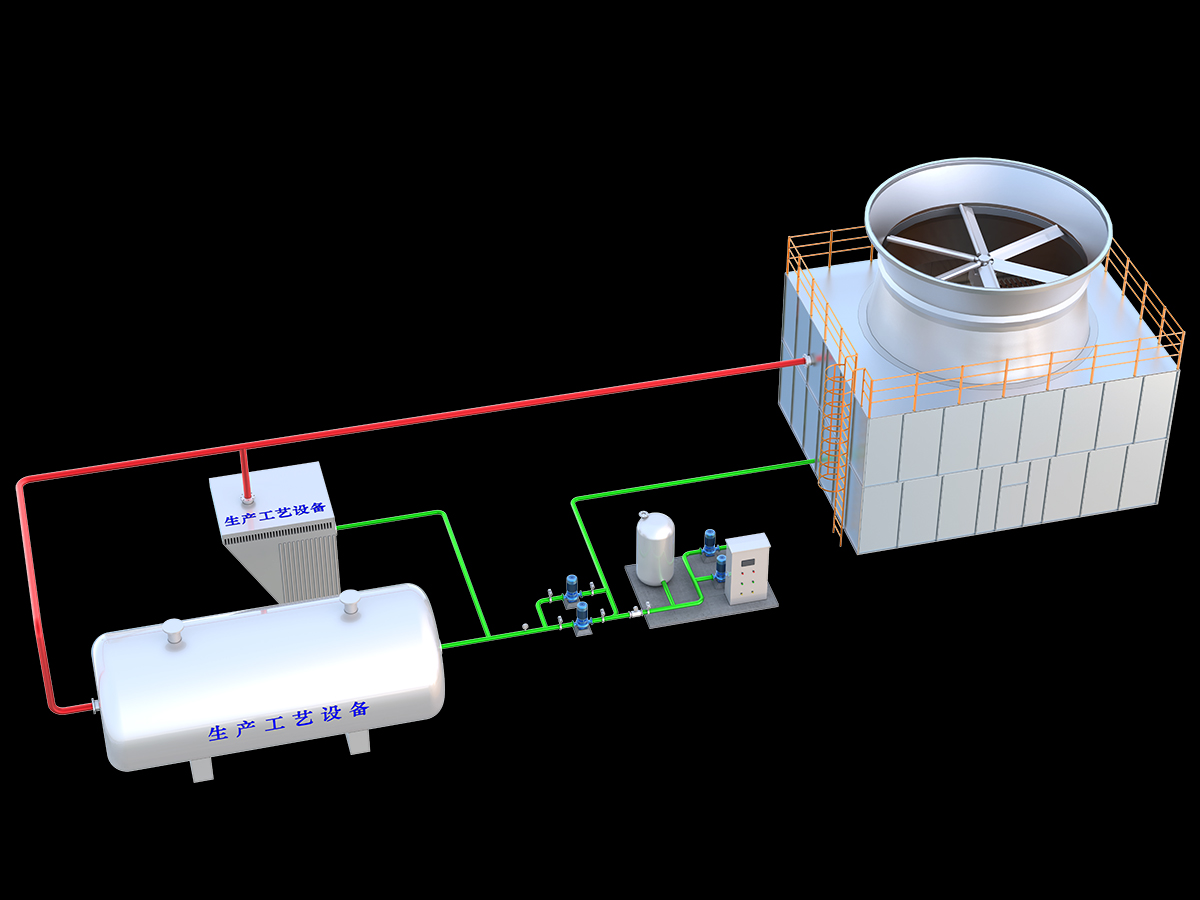

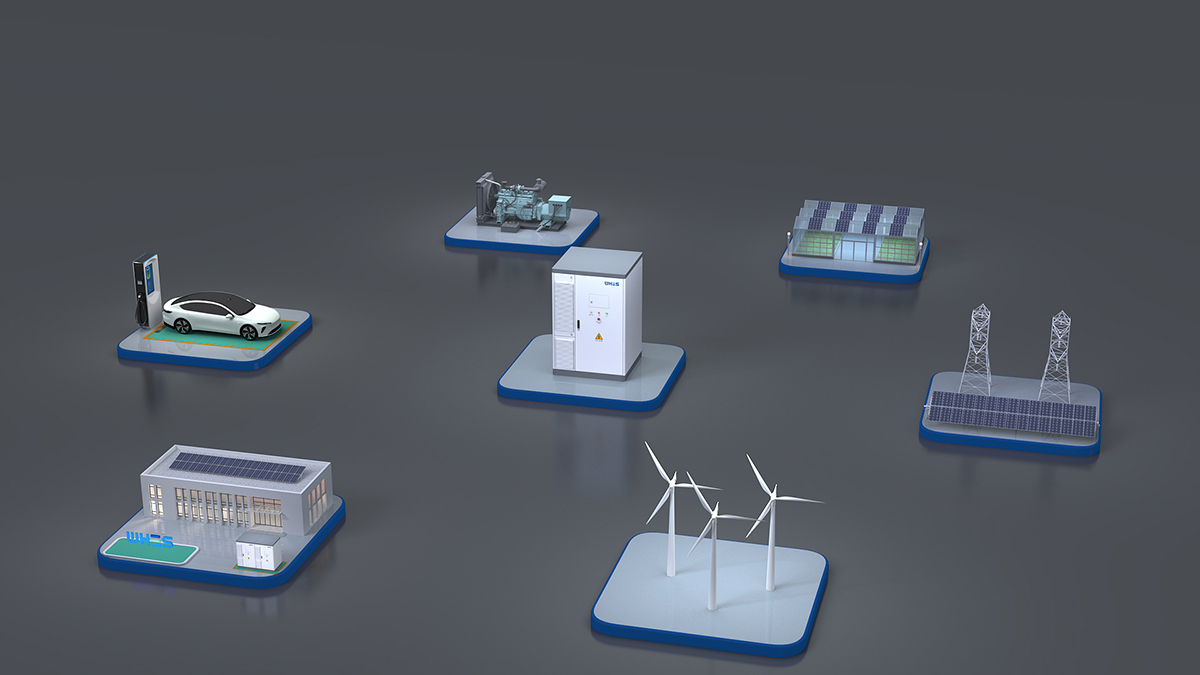

工业产品是工业部门生产制造的各类物品,种类繁多,分类方式多样,以下从不同维度为你介绍工业产品的分类:
按生产行业分类
机械工业产品效果图制做
通用机械:如泵、风机、压缩机、阀门等,这些设备广泛应用于各个工业领域。例如,泵用于输送液体,在化工、石油、水处理等行业都不可或缺;风机则用于通风、换气等,在建筑、矿山等领域有大量应用。
专用机械:针对特定行业或工艺需求设计的机械,如纺织机械、印刷机械、食品加工机械等。以纺织机械为例,它包括纺纱机、织布机等,专门用于纺织品的生产,能满足纺织行业独特的工艺要求。
仪器仪表:用于测量、检验、记录和控制各种物理量、化学量等的仪器和设备,如温度计、压力表、流量计、分析仪器等。在工业生产中,仪器仪表能实时监测生产过程中的各种参数,确保产品质量和生产安全。
电子信息工业产品效果图制做
电子元器件:是构成电子设备的基本单元,如电阻、电容、电感、二极管、三极管、集成电路等。这些元器件虽小,但在电子设备中起着至关重要的作用,例如集成电路,它集成了大量的电子元件,能实现复杂的电路功能,是现代电子设备的核心部件。
电子设备效果图制做:包括通信设备(如手机、基站等)、计算机(如台式电脑、笔记本电脑等)、消费电子(如电视、音响、数码相机等)。以手机为例,它集成了通信、计算、娱乐等多种功能,成为人们日常生活中不可或缺的工具。
软件产品:如操作系统、办公软件、工业控制软件、游戏软件等。软件产品与硬件设备相互配合,为人们提供各种服务和功能。例如,工业控制软件能实现对生产设备的自动化控制,提高生产效率和质量。
化工工业产品效果图制做
基本化工原料:如乙烯、丙烯、苯、甲醇等,这些原料是生产其他化工产品的基础。例如,乙烯可用于生产聚乙烯、聚氯乙烯等多种塑料产品。
化学肥料:包括氮肥、磷肥、钾肥、复合肥等,用于提高土壤肥力,促进农作物生长。如尿素是一种常见的氮肥,能提供植物生长所需的氮元素。
化学农药:用于防治农作物病虫害,保障农作物的产量和质量。例如,杀虫剂可以杀死害虫,杀菌剂可以防治植物病害。
合成材料:如塑料、合成纤维、合成橡胶等。塑料具有质轻、耐腐蚀、易加工等特点,广泛应用于包装、建筑、电子等领域;合成纤维如涤纶、锦纶等,具有强度高、耐磨性好等优点,常用于制作服装、绳索等。
轻工工业产品
日用消费品:如家具、家电、服装、鞋帽、化妆品、洗涤用品等。这些产品与人们的日常生活密切相关,满足了人们的基本生活需求。例如,冰箱用于储存食物,洗衣机用于清洗衣物,化妆品则用于美化个人形象。
文体用品:包括文具(如笔、本子、书包等)、体育用品(如篮球、足球、健身器材等)、乐器(如钢琴、吉他等)。文体用品丰富了人们的精神文化生活,促进了人们的身心健康。
按产品用途分类
原材料:指未经加工或仅经过初步加工,用于进一步生产其他产品的物质,如矿石、木材、棉花、石油等。矿石是冶炼金属的原料,木材可用于制作家具、纸张等,棉花是纺织工业的重要原料,石油则是化工、能源等行业的基础原料。
中间产品:在生产过程中,用于制造最终产品的半成品或零部件。例如,汽车发动机是汽车制造的中间产品,它需要进一步与其他零部件组装成完整的汽车。
最终产品:直接提供给消费者使用,满足其最终需求的产品。如前面提到的手机、电视、服装等,消费者购买这些产品后可以直接使用,无需再进行进一步的加工或组装。
按产品技术含量分类
传统工业产品:这类产品技术相对成熟,生产工艺较为稳定,如一些简单的机械零件、传统的日用品等。它们在市场上已经存在了较长时间,生产技术和市场需求都相对稳定。
高新技术工业产品:采用了先进的技术和创新的设计,具有较高的技术含量和附加值。例如,新能源汽车、人工智能机器人、3D打印设备等。这些产品往往融合了多个领域的先进技术,代表了工业发展的最新方向。
3D产品渲染图通过虚拟建模、材质模拟和光影渲染技术,能够为高附加值、结构复杂、定制化需求强、创新设计导向的产品类别带来质的改变。以下为具体分析:
1. 高附加值产品
典型类别:珠宝、奢侈品、高端电子产品(如智能手机、智能手表)
改变原因:
材质真实还原:3D渲染可模拟珠宝的金属光泽、宝石的折射效果,或高端电子产品的金属边框、玻璃屏幕质感,提升消费者对产品品质的信任感。
细节展示:通过高精度渲染,突出产品的工艺细节(如珠宝的镶嵌工艺、电子产品的精密结构),增强品牌价值。
案例:苹果公司常通过3D渲染展示iPhone的金属边框和玻璃背板,强化“高端科技”形象。
2. 结构复杂或不可直接观察的产品
典型类别:机械设备、工业零部件、医疗设备(如CT扫描仪、心脏起搏器)
改变原因:
内部结构可视化:3D渲染可拆解产品,展示内部机械结构或电路设计,帮助用户理解产品功能。
技术参数可视化:通过渲染图标注尺寸、材质或技术参数,提升专业用户的决策效率。
案例:医疗器械公司通过3D渲染展示心脏起搏器的内部结构,帮助医生理解其工作原理。
3. 定制化或个性化需求强的产品
典型类别:家具、服装、汽车内饰、个性化电子产品(如定制键盘)
改变原因:
快速预览定制效果:用户可通过3D渲染实时调整产品颜色、材质或图案,降低定制成本。
减少沟通成本:设计师可直接通过渲染图与客户确认需求,避免反复修改实物样品。
案例:宜家通过3D渲染展示家具的定制化选项(如颜色、尺寸),提升用户体验。
4. 创新设计或概念产品
典型类别:未来概念汽车、智能穿戴设备、智能家居产品(如智能机器人)
改变原因:
设计理念传达:3D渲染可将抽象的设计概念转化为可视化图像,帮助用户理解产品的未来感或科技感。
市场测试:通过渲染图进行市场调研,收集用户反馈,优化产品设计。
案例:特斯拉通过3D渲染展示Cybertruck的未来感设计,引发全球关注。
5. 虚拟体验或沉浸式需求强的产品
典型类别:游戏硬件、VR设备、AR应用相关产品
改变原因:
沉浸式展示:3D渲染可结合虚拟现实(VR)或增强现实(AR)技术,让用户身临其境地体验产品功能。
交互式展示:用户可通过3D渲染图与产品进行互动(如旋转、缩放),提升参与感。
案例:Oculus通过3D渲染展示VR头显的佩戴效果和游戏场景,增强用户购买欲望。
6. 建筑或空间相关产品
典型类别:室内设计、家具、灯具、智能家居系统
改变原因:
空间适配性展示:3D渲染可将产品融入虚拟空间,展示其与环境的适配性(如家具在房间中的摆放效果)。
光影效果模拟:通过渲染模拟不同时间的光照效果,帮助用户理解产品的实际使用场景。
Industrial products are various items produced and manufactured by the industrial sector, with a wide variety of types and diverse classification methods. The following introduces the classification of industrial products from different dimensions:
Classified by production industry
Production of renderings for mechanical industry products
General machinery, such as pumps, fans, compressors, valves, etc., are widely used in various industrial fields. For example, pumps are used to transport liquids and are indispensable in industries such as chemical, petroleum, and water treatment; Fans are used for ventilation, air exchange, and have a wide range of applications in fields such as construction and mining.
Specialized machinery: machinery designed for specific industries or process requirements, such as textile machinery, printing machinery, food processing machinery, etc. Taking textile machinery as an example, it includes spinning machines, weaving machines, etc., which are specifically used for the production of textiles and can meet the unique process requirements of the textile industry.
Instrumentation: Instruments and equipment used for measuring, inspecting, recording, and controlling various physical and chemical quantities, such as thermometers, pressure gauges, flow meters, analytical instruments, etc. In industrial production, instruments and meters can monitor various parameters in real-time to ensure product quality and production safety.
Production of renderings for electronic information industry products
Electronic components: They are the basic units that make up electronic devices, such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, transistors, integrated circuits, etc. Although these components are small, they play a crucial role in electronic devices, such as integrated circuits, which integrate a large number of electronic components and can achieve complex circuit functions. They are the core components of modern electronic devices.
Electronic device rendering: including communication devices (such as mobile phones, base stations, etc.), computers (such as desktop computers, laptops, etc.), and consumer electronics (such as televisions, speakers, digital cameras, etc.). Taking mobile phones as an example, they integrate various functions such as communication, computing, and entertainment, becoming an indispensable tool in people's daily lives.
Software products: such as operating systems, office software, industrial control software, game software, etc. Software products and hardware devices work together to provide people with various services and functions. For example, industrial control software can achieve automated control of production equipment, improving production efficiency and quality.
Production of renderings for chemical industry products
Basic chemical raw materials, such as ethylene, propylene, benzene, methanol, etc., are the basis for producing other chemical products. For example, ethylene can be used to produce various plastic products such as polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride.
Chemical fertilizers: including nitrogen fertilizer, phosphorus fertilizer, potassium fertilizer, compound fertilizer, etc., used to improve soil fertility and promote crop growth. Urea is a common nitrogen fertilizer that can provide the nitrogen elements needed for plant growth.
Chemical pesticides: used for preventing and controlling crop diseases and pests, ensuring crop yield and quality. For example, insecticides can kill pests, and fungicides can prevent and control plant diseases.
Synthetic materials: such as plastic, synthetic fibers, synthetic rubber, etc. Plastic has the characteristics of light weight, corrosion resistance, and easy processing, and is widely used in packaging, construction, electronics, and other fields; Synthetic fibers such as polyester and nylon have the advantages of high strength and good wear resistance, and are commonly used in the production of clothing, ropes, etc.
Light industrial products
Daily consumer goods: such as furniture, household appliances, clothing, shoes and hats, cosmetics, washing products, etc. These products are closely related to people's daily lives and meet their basic living needs. For example, refrigerators are used to store food, washing machines are used to clean clothes, and cosmetics are used to enhance personal image.
Sports supplies: including stationery (such as pens, notebooks, backpacks, etc.), sports equipment (such as basketball, soccer, fitness equipment, etc.), musical instruments (such as piano, guitar, etc.). Cultural and sports supplies enrich people's spiritual and cultural life, and promote their physical and mental health.
Classified by product usage
Raw materials: Refers to substances that have not been processed or have only undergone preliminary processing, used for further production of other products, such as ore, wood, cotton, petroleum, etc. Ore is the raw material for smelting metals, wood can be used to make furniture, paper, etc. Cotton is an important raw material for the textile industry, and petroleum is the basic raw material for industries such as chemical and energy.
Intermediate product: a semi-finished product or component used in the production process to manufacture the final product. For example, a car engine is an intermediate product in car manufacturing that needs to be further assembled with other components to form a complete car.
Final product: a product directly provided to consumers to meet their ultimate needs. As mentioned earlier, products such as mobile phones, televisions, and clothing can be used directly by consumers after purchase without further processing or assembly.
Classified by product technical content
Traditional industrial products: These products have relatively mature technology and stable production processes, such as some simple mechanical parts, traditional daily necessities, etc. They have been in the market for a long time, with relatively stable production technology and market demand.
High tech industrial products: adopting advanced technology and innovative design, with high technological content and added value. For example, new energy vehicles, artificial intelligence robots, 3D printing equipment, etc. These products often integrate advanced technologies from multiple fields, representing the latest direction of industrial development.
3D product rendering can bring qualitative changes to product categories with high added value, complex structure, strong customization requirements, and innovative design orientation through virtual modeling, material simulation, and light and shadow rendering technology. The following is a specific analysis:
1. High value-added products
Typical categories: jewelry, luxury goods, high-end electronic products (such as smartphones, smartwatches)
Reason for change:
Realistic reproduction of materials: 3D rendering can simulate the metallic luster of jewelry, the refractive effect of gemstones, or the metal frame and glass screen texture of high-end electronic products, enhancing consumers' trust in product quality.
Detail display: Through high-precision rendering, highlight the craftsmanship details of the product (such as jewelry inlay technology, precision structure of electronic products), and enhance brand value.
Case: Apple often uses 3D rendering to showcase the metal frame and glass back panel of the iPhone, enhancing the image of "high-end technology".
2. Products with complex structures or those that cannot be directly observed
Typical categories: mechanical equipment, industrial components, medical equipment (such as CT scanners, pacemakers)
Reason for change:
Internal structure visualization: 3D rendering of detachable products, showcasing internal mechanical structures or circuit designs, helping users understand product functionality.
Visualization of Technical Parameters: By rendering graphics with annotations of size, material, or technical parameters, professional users can improve their decision-making efficiency.
Case: A medical device company uses 3D rendering to showcase the internal structure of a pacemaker, helping doctors understand its working principle.
3. Products with strong customization or personalized needs
Typical categories: Furniture, Clothing, Automotive Interiors, Personalized Electronic Products (such as Customized Keyboard)
Reason for change:
Quick preview of customized effects: Users can adjust product colors, materials, or patterns in real-time through 3D rendering, reducing customization costs.
Reduce communication costs: Designers can directly confirm requirements with clients through rendered images, avoiding repeated modifications to physical samples.
Case: IKEA enhances the user experience by displaying customized furniture options (such as color and size) through 3D rendering.
4. Innovative design or conceptual products
Typical categories: Future concept cars, smart wearable devices, smart home products (such as smart robots)
Reason for change:
Design concept communication: 3D rendering can transform abstract design concepts into visual images, helping users understand the futuristic or technological feel of the product.
Market testing: Conduct market research through rendered images, collect user feedback, and optimize product design.
Case: Tesla showcases the futuristic design of Cybertruck through 3D rendering, attracting global attention.
5. Products with strong demand for virtual experiences or immersive experiences
Typical categories: gaming hardware, VR devices, AR application related products
Reason for change:
Immersive display: 3D rendering can be combined with virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR) technology to allow users to experience product functionality in an immersive way.
Interactive display: Users can interact with the product through 3D rendering (such as rotation, scaling) to enhance their sense of participation.
Case: Oculus uses 3D rendering to showcase the wearing effect of VR headsets and game scenes, enhancing users' desire to purchase.
6. Building or space related products
Typical categories: Interior design, furniture, lighting fixtures, smart home systems
Reason for change:
Spatial Adaptability Display: 3D rendering can integrate products into virtual spaces, showcasing their adaptability to the environment (such as the placement of furniture in a room).
Light and shadow effect simulation: By rendering and simulating lighting effects at different times, it helps users understand the actual usage scenarios of the product.



